Source: Home · espressif/ESP8266_AT Wiki
Monthly Archives: September 2021
ESP8266 – AT Command Reference · room-15
ESP8266 – AT Command Reference
ESP8266, in it’s default configuration, boots up into the serial modem mode. In this mode you can communicate with it using a set of AT commands. AT commands that ESP8266 supports, explain what they do and how to use them.
Historically AT commands are based on the Hayes Command Set and these are no different.
AT Commands
Index of all known AT commands
Line termination
ESP8266 expects <CR><LF> or CarriageReturn and LineFeed at the end of each command, but just<CR> seems to work too.
Command variants
Each command can have up to 4 variants changing the function of it. You can chose between them by appending one of four possible values to the end of the root command itself. These four appendices can have the following values "",=<parameter|[parameters]>,"?",=?
| Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Test | AT+CIPSTART=? | Query the range of values (So far only AT+CWMODE=? uses it) |
| Query | AT+CMD? | Returns the current value of the parameter. |
| Set | AT+CMD=Parameter | Set the value of user-defined parameters in commands and run. |
| Execute | AT+CMD | Runs commands with no user-defined parameters. |
Note:
- Not all AT commands support all 4 variants.
- [] = default value, not required or may not appear.
- String values require double quotation marks, for example:
AT+CWSAP="ESP756190","21030826",1,4. - Baud rate = 115200
- AT instruction ends with “\r\n”
Commands
AT – Test AT startup
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | AT | OK | Test if AT system works correctly |
AT+RST – Restart module
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | AT+RST | OK | Reset the module |
ESP-01 Output after reset:
ets Jan 8 2013,rst cause:4, boot mode:(3,7)
wdt reset
load 0x40100000, len 24444, room 16
tail 12
chksum 0xe0
ho 0 tail 12 room 4
load 0x3ffe8000, len 3168, room 12
tail 4
chksum 0x93
load 0x3ffe8c60, len 4956, room 4
tail 8
chksum 0xbd
csum 0xbd
ready
ESP-12 Output after reset:
\0x04B1\0x85 \0xff\0x13:'\0xe0;\0xcc;!G\0xfa\0x11\0xa9R\0xc6\0x83\0x01\0xd9\0x81
[Vendor:www.ai-thinker.com Version:0.9.2.4]
ready
AT+GMR – View version info
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | AT+GMR | version, OK |
Print firmware version |
Parameters:
version: firmware version number
ESP-01 output:
00160901
ESP-12 output:
0018000902-AI03
AT+GSLP – Enter deep-sleep mode
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| set | AT+GSLP=time |
time OK |
Enter deep sleep mode for time milliseconds |
parameters:
time: Time to sleep in milliseconds
Example:
AT+GSLP=1500
Note:
Hardware has to support deep-sleep wake up (Reset pin has to be High).
ATE – Enable / Disable echo
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | ATE0 | OK | Disable echo (Doesn’t send back received command) |
| Execute | ATE1 | OK | Enable echo (Sends back received command before response) |
Note:
I haven’t had any luck with this command yet. Both ATE0 and ATE1 return no this fun.
ATE returns OK
This changed with ESP-12 where the command functions exactly as expected!
AT+CWMODE – WIFI mode(station, AP, station + AP)
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | AT+CWMODE=? | +CWMODE:(1-3) OK | List valid modes |
| Query | AT+CWMODE? | +CWMODE:mode OK |
Query AP’s info which is connect by ESP8266. |
| Execute | AT+CWMODE=mode |
OK | Set AP’s info which will be connect by ESP8266. |
Parameters:
mode: An integer designating the mode of operation either 1, 2, or 3.
1 = Station mode (client)
2 = AP mode (host)
3 = AP + Station mode (Yes, ESP8266 has a dual mode!)
Notes:
ESP-12 came configured as host with ssid set to ESP_A0A3F2, no password, channel 1 You can use AT+CWSAP? to find the current settings.
AT+CWJAP – Connect to AP
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CWJAP? | + CWJAP:ssid OK |
Prints the SSID of Access Point ESP8266 is connected to. |
| Execute | AT+CWJAP=ssid,pwd |
OK | Commands ESP8266 to connect a SSID with supplied password. |
Parameters:
ssid:String, AP’s SSIDpwd:String, not longer than 64 characters
Example:
AT+CWJAP="my-test-wifi","1234test"
Example AT+CWJAP?:
+CWJAP:"my-test-wifi"
AT+CWLAP – Lists available APs
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set | AT+CWLAP=ssid,mac,ch |
+CWLAP:ecn,ssid,rssi,mac OK |
Search available APs with specific conditions. |
| Execute | AT+CWLAP | AT+CWLAP:ecn,ssid,rssi,mac OK |
Lists available Access Points. |
Parameters:
ecn:- 0 = OPEN
- 1 = WEP
- 2 = WPA_PSK
- 3 = WPA2_PSK
- 4 = WPA_WPA2_PSK
ssid: String, SSID of APrssi: signal strengthmac: String, MAC address
Note:
On ESP-01 I have had no luck with the set version of this command (AT+CWLAP=...). If you know what it does please let me know.
On ESP-12, the Set version of the command allows to see if a certain SSID, with certain MAC on certain channel exists. If it doesit is returned as one line of the Execute version of this command.
Example AT+CWLAP:
+CWLAP:(3,"CVBJB",-71,"f8:e4:fb:5b:a9:5a",1)
+CWLAP:(3,"HT_00d02d638ac3",-90,"04:f0:21:0f:1f:61",1)
+CWLAP:(3,"CLDRM",-69,"22:c9:d0:1a:f6:54",1)
+CWLAP:(2,"AllSaints",-88,"c4:01:7c:3b:08:48",1)
+CWLAP:(0,"AllSaints-Guest",-83,"c4:01:7c:7b:08:48",1)
+CWLAP:(0,"AllSaints-Guest",-83,"c4:01:7c:7b:05:08",6)
+CWLAP:(4,"C7FU24",-27,"e8:94:f6:90:f9:d7",6)
+CWLAP:(2,"AllSaints",-82,"c4:01:7c:3b:05:08",6)
+CWLAP:(3,"QGJTL",-87,"f8:e4:fb:b5:6b:b4",6)
+CWLAP:(4,"50EFA8",-78,"74:44:01:50:ef:a7",6)
+CWLAP:(0,"optimumwifi",-78,"76:44:01:50:ef:a8",6)
+CWLAP:(3,"BHQH4",-95,"18:1b:eb:1a:af:5b",6)
+CWLAP:(3,"NETGEAR49",-86,"84:1b:5e:e0:28:03",7)
+CWLAP:(3,"ngHub_319332NW00047",-56,"20:e5:2a:79:b1:2f",11)
+CWLAP:(3,"BFZR4",-73,"18:1b:eb:1d:c3:91",11)
+CWLAP:(1,"5FFVL",-82,"00:26:b8:b5:c0:f2",11)
+CWLAP:(3,"59G6D",-77,"00:7f:28:6d:91:7b",11)
+CWLAP:(3,"N16FU",-53,"20:cf:30:ce:60:fe",11)
+CWLAP:(3,"ITS",-82,"90:72:40:21:5f:76",11)
+CWLAP:(3,"ITS",-79,"24:a2:e1:f0:04:e4",11)
Example AT+CWLAP="N16FU","20:cf:30:ce:60:fe",11:
+CWLAP:(3,"N16FU",-53,"20:cf:30:ce:60:fe",11)
AT+CWQAP – Disconnect from AP
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | AT+CWQAP | OK | Disconnect ESP8266 from the AP is currently connected to. |
Note:
After running this command, if you run AT+CWJAP? it still shows the AP you were connected to before. Back to Index
AT+CWSAP – Configuration of softAP mode
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CWSAP? | +CWSAP:ssid,pwd,ch,ecn OK |
Query configuration of ESP8266 softAP mode. |
| Set | AT+CWSAP=ssid,pwd,ch,ecn |
OK | Set configuration of softAP mode. |
Parameters:
ssid: String, ESP8266’s softAP SSIDpwd: String, Password, no longer than 64 charactersch: channel idecn:- 0 = OPEN
- 2 = WPA_PSK
- 3 = WPA2_PSK
- 4 = WPA_WPA2_PSK
Example
AT+CWSAP="esp_123","1234test",5,3
AT+CWSAP? => +CWSAP:"esp_123","1234test",5,3
AT+CWLIF – List clients connected to ESP8266 softAP
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | AT+CWLIF | [ip,other] OK |
List information on of connected clients. |
Parameters:
ip: IP address of a client connected to the ESP8266 softAP other: Other info, look at example. I don’t know what it means yet.
Example (ESP-01):
AT+CWLIF
192.168.4.100,3fff50b4:3fff50ba:3fff50c0:3fff50c6:3fff50cc:3fff50d2
OK
Example (ESP-12):
AT+CWLIF
192.168.4.100,c0:ee:fb:25:33:ec
OK
I ran the command after connecting to the ESP8266 with my cellphone.
AT+CWDHCP – Enable/Disable DHCP
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set | AT+CWDHCP=mode,en |
OK | Enable or disable DHCP for selected mode |
Parameters:
mode:- 0 : set ESP8266 as a softAP
- 1 : set ESP8266 as a station
- 2 : set both ESP8266 to both softAP and a station
en:- 0 : Enable DHCP
- 1 : Disable DHCP
Note:
This command doesn’t seem to work on firmware 00160901 (ESP-01) nor 0018000902-AI03 (ESP-12).
AT+CIPSTAMAC – Set MAC address of ESP8266 station
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CIPSTAMAC? | +CIPSTAMAC:mac OK |
Print current MAC ESP8266’s address. |
| Execute | AT+CIPSTAMAC=mac |
OK | Set ESP8266’s MAC address. |
Parameters:
mac: String, MAC address of the ESP8266 station.
Example:
AT+CIPSTAMAC="18:aa:35:97:d4:7b"
Note:
This command doesn’t seem to work on firmware 00160901
AT+CIPAPMAC – Set MAC address of ESP8266 softAP
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CIPAPMAC? | +CIPAPMAC:mac OK |
Get MAC address of ESP8266 softAP. |
| Execute | AT+CIPAPMAC=mac |
OK | Set mac of ESP8266 softAP. |
Parameters:
mac: String, MAC address of the ESP8266 softAP.
Example:
AT+CIPAPMAC=”2c:aa:35:97:d4:7b”
Note:
This command doesn’t seem to work on firmware 00160901
AT+CIPSTA – Set IP address of ESP8266 station
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CIPSTA? | +CIPSTA:ip OK |
Get IP address of ESP8266 station. |
| Execute | AT+CIPSTA=ip |
OK | Set ip addr of ESP8266 station. |
Parameters:
ip: String, ip address of the ESP8266 station.
Example:
AT+CIPSTA=”192.168.101.108”
Note:
This command doesn’t seem to work on firmware 00160901
AT+CIPAP – Set ip address of ESP8266 softAP
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CIPAP? | +CIPAP:ip OK |
Get ip address of ESP8266 softAP. |
| Execute | AT+CIPAP=ip |
OK | Set ip addr of ESP8266 softAP. |
Parameters:
ip: String, ip address of ESP8266 softAP.
Example:
AT+CIPAP="192.168.5.1"
Note:
This command doesn’t seem to work on firmware 00160901
AT+CIPSTATUS – Information about connection
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | AT+CIPSTATUS=? | OK | |
| Execute | AT+CIPSTATUS | STATUS:status +CIPSTATUS:id,type,addr,port,tetype OK |
Get information about connection. |
Parameters:
status:- 2: Got IP
- 3: Connected
- 4: Disconnected
id: id of the connection (0~4), for multi-connecttype: String, “TCP” or “UDP”addr: String, IP address.port: port numbertetype:- 0 = ESP8266 runs as a client
- 1 = ESP8266 runs as a server
Note:
On ESP-01 this command returns STATUS:1 instead (no extra info, but status changes) On 0018000902-AI03 this command returns STATUS:2 instead (no extra info, but status changes)
AT+CIPSTART – Establish TCP connection or register UDP port and start a connection
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
| Set | AT+CIPSTART=type,addr,port |
OK | Start a connection as client. (Single connection mode) |
| Set | AT+CIPSTART=id,type,addr,port |
OK | Start a connection as client. (Multiple connection mode) |
| Test | AT+CIPSTART=? | [+CIPSTART:(id)(“type”),(“ip address”),(port)] OK | List possible command variations) |
Parameters:
id: 0-4, id of connectiontype: String, “TCP” or “UDP”addr: String, remote IPport: String, remote port
AT+CIPSEND – Send data
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | AT+CIPSEND=? | OK | |
| Set | AT+CIPSEND=length |
SEND OK | Set length of the data that will be sent. For normal send (single connection). |
| Set | AT+CIPSEND=id,length |
SEND OK | Set length of the data that will be sent. For normal send (multiple connection). |
| Execute | AT+CIPSEND | Send data. For unvarnished transmission mode. |
Normal Mode
Parameters:
id: ID no. of transmit connectionlength: data length, MAX 2048 bytes
Unvarnished Transmission Mode
Wrap return “>” after execute command. Enters unvarnished transmission, 20ms interval between each packet, maximum 2048 bytes per packet. When single packet containing “+++” is received, it returns to command mode.
AT+CIPCLOSE – Close TCP or UDP connection
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | AT+CIPCLOSE=? | OK | |
| Set | AT+CIPCLOSE=id |
OK | Close TCP or UDP connection.For multiply connection mode |
| Execute | AT+CIPCLOSE | OK | Close TCP or UDP connection.For single connection mode |
Parameters:
id: ID no. of connection to close, when id=5, all connections will be closed.
Note:
In server mode, id = 5 has no effect!
AT+CIFSR – Get local IP address
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test | AT+CIFSR=? | OK | |
| Execute | AT+CIFSR | +CIFSR:ip OK |
Get local IP address. |
Parameters:
ip: IP address of the ESP8266 as an client.
Example AT+CIFSR:
10.101.10.134
AT+CIPMUX – Enable multiple connections or not
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set | AT+CIPMUX=mode |
OK | Enable / disable multiplex mode (up to 4 conenctions) |
| Query | AT+CIPMUX? | +CIPMUX:mode OK |
Print current multiplex mode. |
Parameters:
mode:- 0: Single connection
- 1: Multiple connections (MAX 4)
NOTE:
This mode can only be changed after all connections are disconnected. If server is started, reboot is required.
AT+CIPSERVER – Configure as server
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Set | AT+CIPSERVER=mode[,port] |
OK | Configure ESP8266 as server |
Parameters:
mode:- 0: Delete server (need to follow by restart)
- 1: Create server
port: port number, default is 333
NOTE:
- Server can only be created when AT+CIPMUX=1
- Server monitor will automatically be created when Server is created.
- When a client is connected to the server, it will take up one connection,be gave an id.
AT+CIPMODE – Set transfer mode
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CIPMODE? | +CIPMODE:mode OK |
Set transfer mode,normal or transparent transmission. |
| Set | AT+CIPMODE=mode |
OK | Set transfer mode,normal or transparent transmission. |
Parameters:
mode:- 0: normal mode
- 1: unvarnished transmission mode
AT+CIPSTO – Set server timeout
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Query | AT+CIPSTO? | +CIPSTO:time |
Query server timeout. |
| Set | AT+CIPSTO=time |
OK | Set server timeout. |
Parameters:
time: server timeout, range 0~7200 seconds
AT+CIUPDATE – update through network
!!! Don’t run this unless you know what you’re doing !!!
!!! It will likely brick your device !!!
Attempts to self-update from the internet.
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | AT+CIUPDATE | +CIPUPDATE:n OK |
Start update through network |
Parameters:
–n:
- 1: found server
- 2: connect server
- 3: got edition
- 4: start update
Example:
AT+CIUPDATE
+CIUPDATE: 1
+CIUPDATE: 2
+CIUPDATE: 3
+CIUPDATE: 4
\0x02\0x8cl\0x8el\0x8e\0x1cp\0x0c\0x8c\0xf2nn\0xee\0x00l\0x8c\0x8el`
\0x02\0x90\0x12\0x12nnl\0x8cl`\0x02\0x0e\0x02nr\0x8e\0x92\0x92n\0x0c\0x0c
\0x02\0x8c\0x92`\0x02`
\0xf2n\0x0c\0x0c\0x0c\0x9e\0xe0b\0x82nl\0x8c\0x0c\0x8c
\0xf2nn\0xee\0x00\0x0c\0x8e\0x0elp\0xf2n\0xe0\0x10\0x02\0x0c
\0x0cr\0x8c\0x9c\0x9c\0xe2\0xe0\0x0c\0x0c\0x0c
\0x0cb\0x0cn\0xe2|\0x02\0xec\0xecl\0x8c\0x0cb\0x8c\0xf2nn
...forever
+IPD – Receive network data
| Variant | Command | Response | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execute | +IPD,len:data |
Receive network data from single connection. | |
| Execute | +IPD,id,len:data |
Receive network data from multiple connection. |
Parameters:
id: id no. of connectionlen: data lengthdata: data received
Note:
I have had no luck with this command so far.
Sources
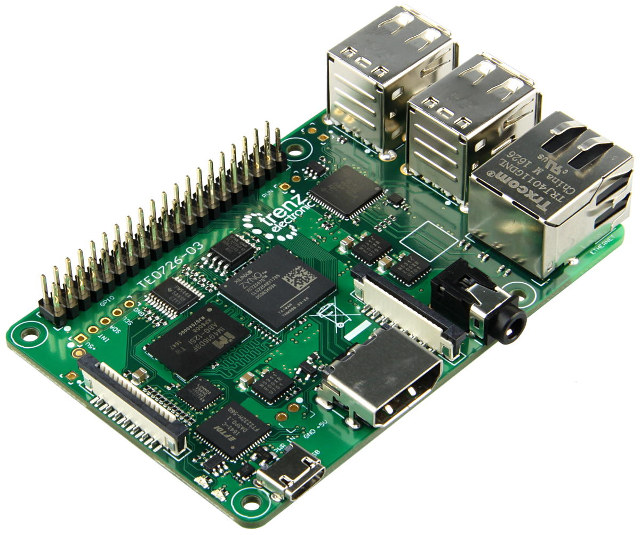
Zynqberry, a Xilinx Zynq FPGA Board with Raspberry Pi 2/3 Form Factor
Earlier this year, I wrote about Trenz Electronic’s Xilinx Zynq Ultrascale+ system-on-module, but I’ve just found out I missed another interesting product
Source: Meet Zynqberry, a Xilinx Zynq FPGA Board with Raspberry Pi 2/3 Form Factor – CNX Software
Orbit/Pan Settings in Fusion 360
Fusion 360
- Zoom: roll the middle mouse button or Ctrl + Shift + middle mouse button
- Pan: middle mouse button
- Orbit: Shift + middle mouse button
Alias
- Zoom: Shift + Alt + right mouse button
- Pan: Shift + Alt + middle mouse button
- Orbit: Shift + Alt + left mouse button
Inventor (Windows only)
- Zoom: F3 + left mouse button
- Pan: F2 + left mouse button
- Orbit: F4 + left mouse button
SolidWorks
- Zoom: Shift + roll middle mouse button
- Pan: Ctrl + middle mouse button (Windows) or Command + middle mouse button (Mac)
- Orbit: Middle mouse button
Tinkercad
- Zoom: roll the middle mouse button or Ctrl + Shift + middle mouse button
- Pan: middle mouse button
- Orbit: right mouse button
Source: Tech Tip: How to Quickly Customize Orbit/Pan Settings in Fusion 360 – Fusion 360 Blog
How to Install Windows 11 Home With a Local Account – ExtremeTech
When you see the “Let’s connect you to a network” screen, hit Shift-F10, type “taskmgr” in the command prompt window, and kill the process called “Network connection flow.” According to the video, this will allow the OS to install normally after you insert a user login and password. You can also kill the application directly from the command line if you like, using the command “taskkill /F /IM oobenetworkconnectionflow.exe”
Source: How to Install Windows 11 Home With a Local Account – ExtremeTech
How to Unlock SPA2102
To reset the SPA-2102 to factory defaults follow these steps:
Plug in power adapter.
Plug in a phone to ‘Phone 1′ port of the SPA-2102.
Dial **** You should hear ‘Configuration Option Menu’.
Dial 73738# (RESET#) Press 1 to confirm the reset.
The SPA-2102 should now have been reset to factory default settings.
You may need to do the following to set up web management depending on which interface you are coming in on:
Dial **** into the phone connected to the ATA device. You should hear ‘Configuration Option Menu’.
Dial 7932 then press 1 to enable. Hang up when you hear option saved.
2. Get access to your SPA-2102 web interface. Plug in Ethernet cable to router and wait for several seconds.
Dial ****110# Listen to IP Address which is read back to you.
Plug your PC into the LAN (Ethernet) port of the SPA-2102. Enter IP Address into your web browser (For example. http://192.168.1.10). You should now see the Linksys SPA-2102 Web Interface
Pandoc a universal document converter
If you need to convert files from one markup format into another, pandoc is your swiss-army knife.
Source: Pandoc – About pandoc
Syntax highlighting for the Web – highlight.js
Syntax highlighting for the Web
Source: highlight.js