How to view and add new entries to the TrustedHosts list using PowerShell on Windows Server 2016.
When you need to enable remote management of a computer or server through WinRM (Windows Remote Management), especially in a Workgroup environment, you should first add computers to the TrustedHosts list. Otherwise, you may most likely encounter errors when communicating between the two sides.
Using PowerShell, you can see what the current records are in the TrustedHosts file but also how to add new records depending on your scenario. You will need to be a member of the Administrators group and run PowerShell commands with administrator rights to make changes to the file.
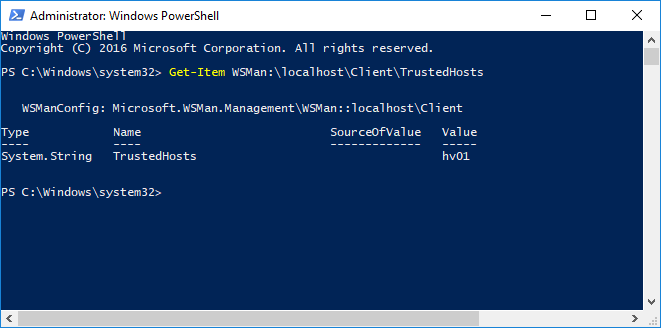
View the computers of TrustedHosts list
To view the list of TrustedHosts added to the machine, type the following command. By default, its value is blank.
Get-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts |
Add all computers to the TrustedHosts list
Using the Set-Item cmdlet and the wildcard you can add all the computers to the TrustedHosts list with the following command.
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value * |
Add all domain computers to the TrustedHosts list
In the following command, replace .yourdomain.com with your own domain name.
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts *.yourdomain.com |
Add specific computers to the TrustedHosts list
You can add specific computers you choose based on their hostname by separating them with a comma (,) using the following command.
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value <ComputerName>,[<ComputerName>] |
Where ComputerName can be in the Server01 or Server01.yourdomain.com format
Add a computer to an existing list of TrustedHosts
If you have already added some computers to the TrustedHosts list and want to add an additional computer, without deleting the previous entries, you should use the following method. This is because the TrustedHosts list is updated based on the last Set-Item command you have run overwriting the previous entries.
Use the following command to save the current TrustedHosts computer list to a curList variable.
$curList = (Get-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts).value |
To add a computer to the current list, type the following command by specifying both the variable you created and the computer name you are going to add.
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value "$curList, Server01" |
Alternatively, to avoid using a variable, add the -Concatenate switch to the Set-Item command to add both new and previous entries. For example:
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Concatenate -Value Server02 |
Add computers to the TrustedHosts list using the IP address
Similarly to the previous commands, you can use an IPv4 or IPv6 address. In the case of IPv6, you have to type the address between [].
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\Client\TrustedHosts -Value 10.10.10.1,[0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0] |
That’s it!
Source: Add computers to TrustedHosts list using PowerShell – Dimitris Tonias