Note: Might be easier to install the admx admin templates to Group Policy Editor. See this post for more info
Office 2019 annoyingly wants you to sign in to either a domain or the cloud. It shares the same registry space as Office 2016, so the procedure is:
Preparation:
1. Note that this must be done on a per-user basis, for anyone who logins into the machine. So 2 users on the same machine = do it twice. Or if that user signs into another machine, do it again.
2. Go into one of the Office apps, go to Account, and select “Sign out” & then click Yes when prompted.First, close all Office applications:
Word
Excel
PowerPoint
Outlook
etc.Second, open the Registry Editor: (may need to Run As Admin)
Start > Run > regedit
Third, navigate down the tree:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER
SOFTWARE
Microsoft
Office
16.0
CommonThird, add the SignIn folder:
Right-click on the Common folder
Go to New > Key
Name it “SignIn” (without the quotes)Fourth, add the registry key to disable the sign-in option:
Right-click on the SignIn folder
Go to New > DWORD (32-bit) VALUE
Name it “SignInOptions” (without the quotes)
Set the value to 3Fifth, verify that it worked:
Open up Word
It should no longer have the “Sign in” button in the top bar
Under File > Account, all of the sign-in verbage should be goneIf you ever need to add it back in, just delete the SignInOptions reg key!
Category Archives: sysadmin
Remote Desktop Services Shortcut Keys – Win32 apps | Microsoft Docs
Notepad++ icons
Could not authenticate to SMB share with correct creds [solved] : freenas
Could not authenticate to SMB share with correct creds [solved]
I solved this issue but wanted to share the solution.
I had set SMB permissions correctly according to this forum post and this video, but I was never able to access my SMB share.
I was able to see the server and the list of shares, but no matter what I could not actually open a share. No matter what user or group I used, each login from W10 would fail with ‘Access is Denied’ or ‘Incorrect user name or password’ or ‘Check with system admin to verify permissions’.
The first thing I wish I had known off the bat was that samba activity is logged in FreeNAS at /var/log/samba4/log.smbd. Tailing that log, it was obvious there were authentication issues. On each login attempt, I saw:
[2018/04/15 02:10:51.243374, 2] ../source3/param/loadparm.c:2787(lp_do_section) Processing section "[$fnstorage]" [2018/04/15 02:10:51.245286, 2] ../libcli/auth/ntlm_check.c:430(ntlm_password_check) ntlm_password_check: NTLMv1 passwords NOT PERMITTED for user msUser [2018/04/15 02:10:51.245752, 2] ../source3/auth/auth.c:332(auth_check_ntlm_password) check_ntlm_password: Authentication for user [msUser] -> [msUser] FAILED with error NT_STATUS_WRONG_PASSWORD, authoritative=1 [2018/04/15 02:10:51.245837, 2] ../auth/auth_log.c:760(log_authentication_event_human_readable) Auth: [SMB2,(null)] user [MicrosoftAccount]\[msUser] at [Sun, 15 Apr 2018 02:10:51.245799 PDT] with [NTLMv1] status [NT_STATUS_WRONG_PASSWORD] workstation [win10-PC] remote host [remoteAddress] mapped to [MicrosoftAccount]\[msUser]. local host [hostAddress] [2018/04/15 02:10:51.245934, 2] ../auth/gensec/spnego.c:605(gensec_spnego_server_negTokenTarg) SPNEGO login failed: NT_STATUS_WRONG_PASSWORDNow at first glance, what jumps out is NT_STATUS_WRONG_PASSWORD, you might think you’re just typing your password wrong. But that’s not what’s really going on– the real culprit is
ntlm_password_check: NTLMv1 passwords NOT PERMITTED for user msUserYou may remember that NTLMv2 is the standard for SMB security, and NTLMv1 authentication is disabled by default in FreeNAS SMB shares.
I figured my PC was using NTLMv1 for some reason. A little research led me to this GPO in Group Policy:
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Security Options\LAN Manager authentication level\Set this to Send NTLMv2 Only instead of whatever else it is. Mine was set to Use NTLMv2 if negotiated. See Microsoft’s docs for the caveats here.
I’m not sure if the value my PC was using is default, and I’m not sure if FreeNAS should actually negotiate NTLMv2, but this resolved my issue with no impact to other SMB shares on my network.
How to detect, enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows | Microsoft Docs
How to detect, enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
This article describes how to enable and disable Server Message Block (SMB) version 1 (SMBv1), SMB version 2 (SMBv2), and SMB version 3 (SMBv3) on the SMB client and server components.
While disabling or removing SMBv1 might cause some compatibility issues with old computers or software, SMBv1 has significant security vulnerabilities and we strongly encourage you not to use it.
Disabling SMBv2 or SMBv3 for troubleshooting
We recommend keeping SMBv2 and SMBv3 enabled, but you might find it useful to disable one temporarily for troubleshooting. For more information, see How to detect status, enable, and disable SMB protocols on the SMB Server.
In Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012, disabling SMBv3 deactivates the following functionality:
- Transparent Failover – clients reconnect without interruption to cluster nodes during maintenance or failover
- Scale Out – concurrent access to shared data on all file cluster nodes
- Multichannel – aggregation of network bandwidth and fault tolerance if multiple paths are available between client and server
- SMB Direct – adds RDMA networking support for high performance, with low latency and low CPU use
- Encryption – Provides end-to-end encryption and protects from eavesdropping on untrustworthy networks
- Directory Leasing – Improves application response times in branch offices through caching
- Performance Optimizations – optimizations for small random read/write I/O
In Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, disabling SMBv2 deactivates the following functionality:
- Request compounding – allows for sending multiple SMBv2 requests as a single network request
- Larger reads and writes – better use of faster networks
- Caching of folder and file properties – clients keep local copies of folders and files
- Durable handles – allow for connection to transparently reconnect to the server if there’s a temporary disconnection
- Improved message signing – HMAC SHA-256 replaces MD5 as hashing algorithm
- Improved scalability for file sharing – number of users, shares, and open files per server greatly increased
- Support for symbolic links
- Client oplock leasing model – limits the data transferred between the client and server, improving performance on high-latency networks and increasing SMB server scalability
- Large MTU support – for full use of 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE)
- Improved energy efficiency – clients that have open files to a server can sleep
The SMBv2 protocol was introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, while the SMBv3 protocol was introduced in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. For more information about SMBv2 and SMBv3 capabilities, see the following articles:
How to remove SMBv1
Here’s how to remove SMBv1 in Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, and Windows 2012 R2.
PowerShell methods
Here are the steps to detect, disable and enable SMBv1 client and server by using PowerShell commands.
Note
The computer will restart after you run the PowerShell commands to disable or enable SMBv1.
- Detect:
PowerShellGet-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol- Disable:
PowerShellDisable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol- Enable:
PowerShellEnable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1ProtocolWindows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019: Server Manager method
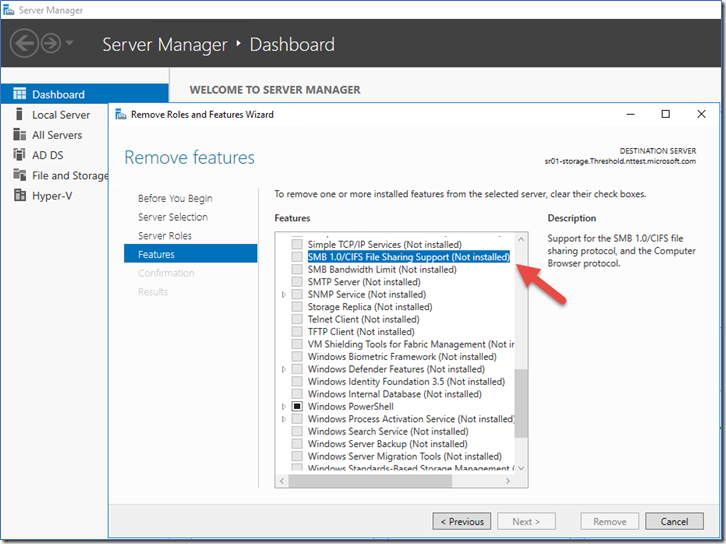
To remove SMBv1 from Windows Server:
- On the Server Manager Dashboard of the server where you want to remove SMBv1, under Configure this local server, select Add roles and features.
- On the Before you begin page, select Start the Remove Roles and Features Wizard, and then on the following page, select Next.
- On the Select destination server page under Server Pool, ensure that the server you want to remove the feature from is selected, and then select Next.
- On the Remove server roles page, select Next.
- On the Remove features page, clear the check box for SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support and select Next.
- On the Confirm removal selections page, confirm that the feature is listed, and then select Remove.
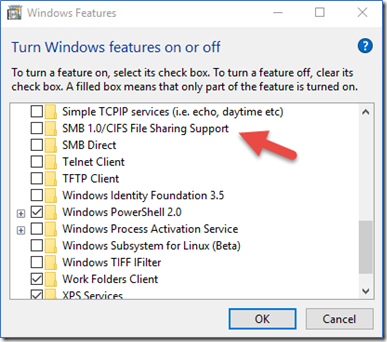
Windows 8.1 and Windows 10: Add or Remove Programs method
To disable SMBv1 on Windows 8.1 and Windows 10:
- In Control Panel, select Programs and Features.
- Under Control Panel Home, select Turn Windows features on or off to open the Windows Features box.
- In the Windows Features box, scroll down the list, clear the check box for SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support and select OK.
- After Windows applies the change, on the confirmation page, select Restart now.
How to detect status, enable, and disable SMB protocols on the SMB Server
For Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10, and Windows Server 2019
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 introduced the new Set-SMBServerConfiguration Windows PowerShell cmdlet. The cmdlet enables you to enable or disable the SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 protocols on the server component.
Note
When you enable or disable SMBv2 in Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012, SMBv3 is also enabled or disabled. This behavior occurs because these protocols share the same stack.
You don’t have to restart the computer after you run the Set-SMBServerConfiguration cmdlet.
SMBv1 on SMB Server
- Detect:
PowerShellGet-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1Protocol- Disable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $false- Enable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $trueFor more information, see Server storage at Microsoft.
SMB v2/v3 on SMB Server
- Detect:
PowerShellGet-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB2Protocol- Disable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $false- Enable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $trueFor Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, and Windows Server 2008
To enable or disable SMB protocols on an SMB Server that is running Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Vista, or Windows Server 2008, use Windows PowerShell or Registry Editor.
PowerShell methods
Note
This method requires PowerShell 2.0 or later version of PowerShell.
SMBv1 on SMB Server
Detect:
PowerShellGet-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}Default configuration = Enabled (No registry named value is created), so no SMB1 value will be returned
Disable:
PowerShellSet-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -ForceEnable:
PowerShellSet-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -ForceNote You must restart the computer after you make these changes. For more information, see Server storage at Microsoft.
SMBv2/v3 on SMB Server
Detect:
PowerShellGet-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath}Disable:
PowerShellSet-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -ForceEnable:
PowerShellSet-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters" SMB2 -Type DWORD -Value 1 -ForceNote
You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
Registry Editor
Important
Follow the steps in this section carefully. Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly. Before you modify it, back up the registry for restoration in case problems occur.
To enable or disable SMBv1 on the SMB server, configure the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB1 REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled Default: 1 = Enabled (No registry key is created)To enable or disable SMBv2 on the SMB server, configure the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
Registry entry: SMB2 REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled REG_DWORD: 1 = Enabled Default: 1 = Enabled (No registry key is created)Note
You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
How to detect status, enable, and disable SMB protocols on the SMB Client
Here is how to detect status, enable, and disable SMB protocols on the SMB Client that is running Windows 10, Windows Server 2019, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012.
Note
When you enable or disable SMBv2 in Windows 8 or in Windows Server 2012, SMBv3 is also enabled or disabled. This behavior occurs because these protocols share the same stack.
SMBv1 on SMB Client
- Detect
Consolesc.exe qc lanmanworkstation- Disable:
Consolesc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb20/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= disabled- Enable:
Consolesc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb10 start= autoFor more information, see Server storage at Microsoft
SMBv2/v3 on SMB Client
- Detect:
Consolesc.exe qc lanmanworkstation- Disable:
Consolesc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= disabled- Enable:
Consolesc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/mrxsmb20/nsi sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start= autoNote
- You must run these commands at an elevated command prompt.
- You must restart the computer after you make these changes.
Disable SMBv1 by using Group Policy
This section introduces how to use Group Policy to disable SMBv1. You can use this method on different versions of Windows.
Disable SMBv1 server
This procedure configures the following new item in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- Registry entry: SMB1
- REG_DWORD: 0 = Disabled
To use Group Policy to configure this, follow these steps:
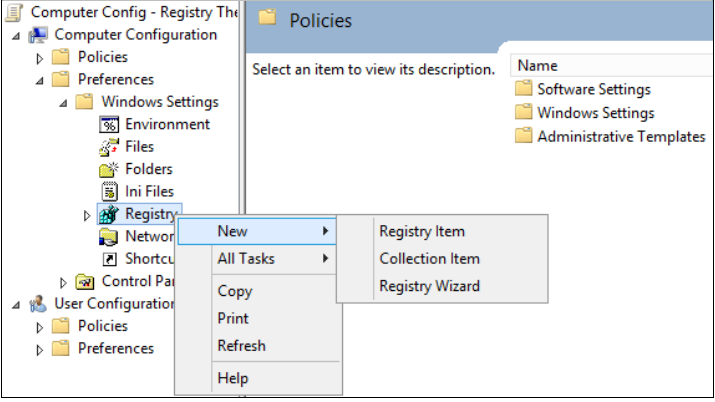
- Open the Group Policy Management Console. Right-click the Group Policy object (GPO) that should contain the new preference item, and then click Edit.
- In the console tree under Computer Configuration, expand the Preferences folder, and then expand the Windows Settings folder.
- Right-click the Registry node, point to New, and select Registry Item.
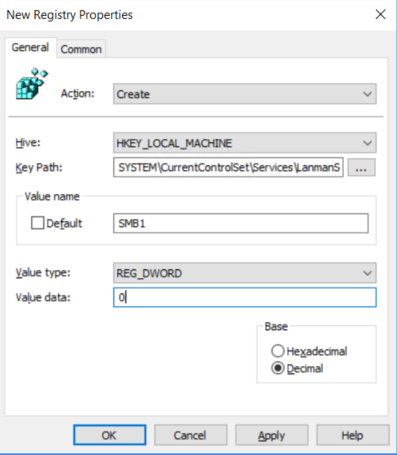
In the New Registry Properties dialog box, select the following:
- Action: Update
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Key Path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters
- Value name: SMB1
- Value type: REG_DWORD
- Value data: 0
This procedure disables the SMBv1 Server components. This Group Policy must be applied to all necessary workstations, servers, and domain controllers in the domain.
Note
WMI filters can also be set to exclude unsupported operating systems or selected exclusions, such as Windows XP.
Important
Be careful when you make these changes on domain controllers on which legacy Windows XP or older Linux and third-party systems (that don’t support SMBv2 or SMBv3) require access to SYSVOL or other file shares where SMB v1 is being disabled.
Disable SMBv1 client
To disable the SMBv1 client, the services registry key needs to be updated to disable the start of MRxSMB10 and then the dependency on MRxSMB10 needs to be removed from the entry for LanmanWorkstation so that it can start normally without requiring MRxSMB10 to first start.
This guidance updates and replaces the default values in the following two items in the registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\mrxsmb10
Registry entry: Start REG_DWORD: 4= Disabled
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation
Registry entry: DependOnService REG_MULTI_SZ: “Bowser”,”MRxSmb20″,”NSI”
Note
The default included MRxSMB10 which is now removed as dependency.
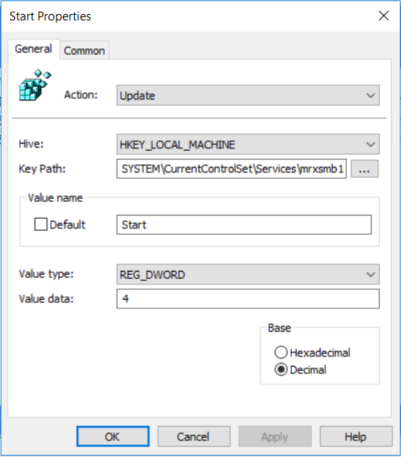
To configure this by using Group Policy, follow these steps:
- Open the Group Policy Management Console. Right-click the GPO that should contain the new preference item, and then click Edit.
- In the console tree under Computer Configuration, expand the Preferences folder, and then expand the Windows Settings folder.
- Right-click the Registry node, point to New, and select Registry Item.
- In the New Registry Properties dialog box, select the following:
- Action: Update
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Key Path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\mrxsmb10
- Value name: Start
- Value type: REG_DWORD
- Value data: 4
- Then remove the dependency on the MRxSMB10 that was disabled.
In the New Registry Properties dialog box, select the following:
- Action: Replace
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
- Key Path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation
- Value name: DependOnService
- Value type: REG_MULTI_SZ
- Value data:
- Bowser
- MRxSmb20
- NSI
Note
These three strings will not have bullets (see the following screen shot).
The default value includes MRxSMB10 in many versions of Windows, so by replacing them with this multi-value string, it is in effect removing MRxSMB10 as a dependency for LanmanWorkstation and going from four default values down to just these three values above.
Note
When you use Group Policy Management Console, you don’t have to use quotation marks or commas. Just type each entry on individual lines.
- Restart the targeted systems to finish disabling SMB v1.
Auditing SMBv1 usage
To determine which clients are attempting to connect to an SMB server with SMBv1, you can enable auditing on Windows Server 2016, Windows 10, and Windows Server 2019. You can also audit on Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 if the May 2018 monthly update is installed, and on Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 if the July 2017 monthly update is installed.
- Enable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -AuditSmb1Access $true- Disable:
PowerShellSet-SmbServerConfiguration -AuditSmb1Access $false- Detect:
PowerShellGet-SmbServerConfiguration | Select AuditSmb1AccessWhen SMBv1 auditing is enabled, event 3000 appears in the “Microsoft-Windows-SMBServer\Audit” event log, identifying each client that attempts to connect with SMBv1.
Summary
If all the settings are in the same GPO, Group Policy Management displays the following settings.
Testing and validation
After completing the configuration steps in this article, allow the policy to replicate and update. As necessary for testing, run gpupdate /force at a command prompt, and then review the target computers to make sure that the registry settings are applied correctly. Make sure SMBv2 and SMBv3 are functioning for all other systems in the environment.
Note
Don’t forget to restart the target systems.
Source: How to detect, enable and disable SMBv1, SMBv2, and SMBv3 in Windows | Microsoft Docs
How to Create a .pem File for SSL Certificate Installations
Creating a .pem File for SSL Certificate Installations
.pem SSL Creation Instructions
SSL .pem files (concatenated certificate container files), are frequently required for certificate installations when multiple certificates are being imported as one file.
This article contains multiple sets of instructions that walk through various .pem file creation scenarios.
Creating a .pem with the Entire SSL Certificate Trust Chain
- You need your Intermediate (CA.crt), Root (TrustedRoot.crt), and Primary Certificates (your_domain_name.crt).
- Open a text editor (such as wordpad) and paste the entire body of each certificate into one text file in the following order:
- The Primary Certificate – your_domain_name.crt
- The Intermediate Certificate – CA.crt
- The Root Certificate – TrustedRoot.crt
Make sure to include the beginning and end tags on each certificate. The result should look like this:
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Primary SSL certificate: your_domain_name.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Intermediate certificate: CA.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Root certificate: TrustedRoot.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–Save the combined file as your_domain_name.pem. The .pem file is now ready to use.
Creating a .pem with the Server and Intermediate Certificates
- You need your Intermediate (CA.crt) and Primary Certificates (your_domain_name.crt).
- Open a text editor (such as wordpad) and paste the entire body of each certificate into one text file in the following order:
- The Primary Certificate – your_domain_name.crt
- The Intermediate Certificate – CA.crt
Make sure to include the beginning and end tags on each certificate. The result should look like this:
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Primary SSL certificate: your_domain_name.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Intermediate certificate: CA.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–Save the combined file as your_domain_name.pem. The .pem file is now ready to use.
Creating a .pem with the Private Key and Entire Trust Chain
- You need your Intermediate (CA.crt) and Primary Certificates (your_domain_name.crt).
- Open a text editor (such as wordpad) and paste the entire body of each certificate into one text file in the following order:
- The Private Key – your_domain_name.key
- The Primary Certificate – your_domain_name.crt
- The Intermediate Certificate – CA.crt
- The Root Certificate – TrustedRoot.crt
Make sure to include the beginning and end tags on each certificate. The result should look like this:
—–BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY—–
(Your Private Key: your_domain_name.key)
—–END RSA PRIVATE KEY—–
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Primary SSL certificate: your_domain_name.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Intermediate certificate: CA.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–
—–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—–
(Your Root certificate: TrustedRoot.crt)
—–END CERTIFICATE—–Save the combined file as your_domain_name.pem. The .pem file is now ready to use.
List of Blue Screen Error Codes (Stop Codes)
List of Blue Screen Error Codes
Complete BSOD error code list from STOP 0x1 to STOP 0xC0000221
How to disable Thunderbird AUTO UPDATE
Disable the auto-update (or app update) process used by (mozilla) Thunderbird = TB, email-client software, and Firefox = FF, web-browser software.
TB = Thunderbird . FF = Firefox.
in below,
if you’ll configure TB only, then avoid following config/setting that are for FF.
if you’ll configure FF only, then avoid following config/setting that are for TB.DISABLE AUTO-UPDATE VIA CONFIG SETTINGS IN THUNDERBIRD/FIREFOX GUI:
Disable auto update via Thunderbird’s (or Firefox’s) GUI (graphical user interfacce):
"about:preferences"– goto TB/FF’s main menu >Preferences(in macOS) , or goto TB/FF main menu >Options(in Windows) , or goto TB/FF main menu >Tools>Options(in Windows), or goto TB main menu >Options(in Linux/Unix).
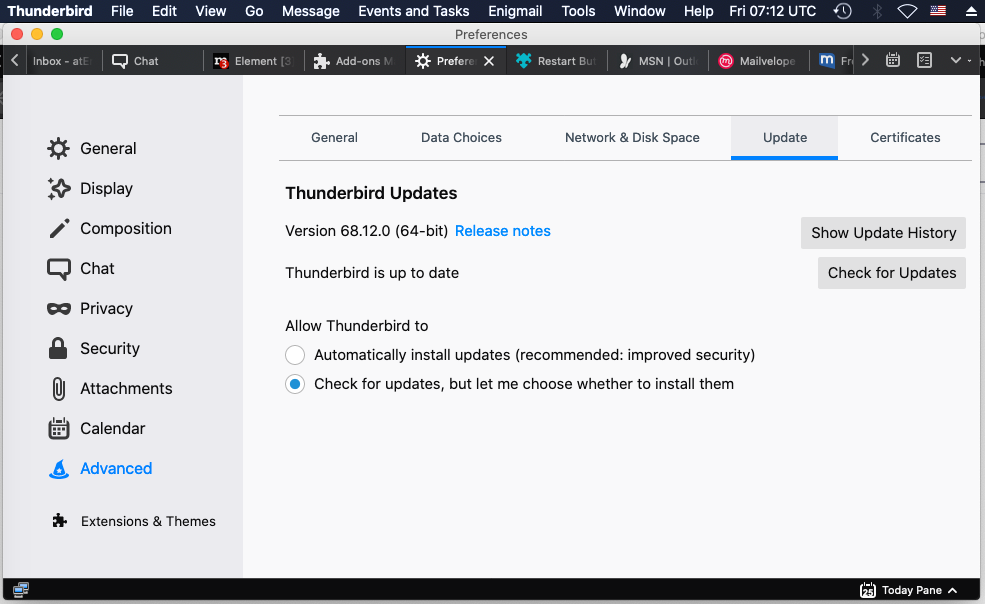
- in macOS goto “Update” tab: in left-pane/rows, select
"Advanced"> then in right-side select"Update"tab- in Windows, Linux/Unix goto “Update” tab or section: select
"General"in left-pane/rows > then in right-side select"Update"tab or scroll-down to the"Update"section.- select this specific option:
◉"check for updates, but let me choose whether to install them".
- if you see such option:
☐“Use a background service to install updates”exists
or has-appeared, under this below option
◉"Check for updates, but let you choose to install them",
then keep the “background-service” option also unchecked/unselected (☐).
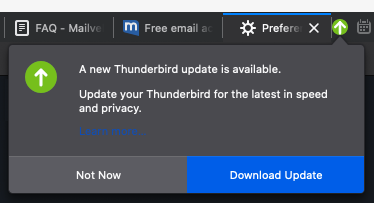
- if this “background-service” option is disabled, and when you will want to do update manually, then TB/FF will show you update pop-ups meesage, and ask you to decide if you want to install or cancel.
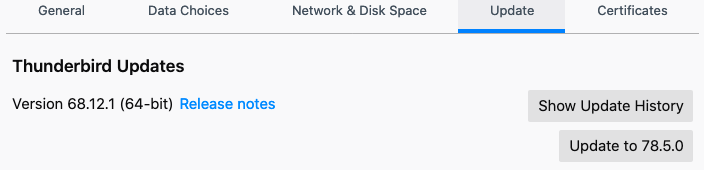
- if you goto “Update” tab or section, you should see info like below
(shown version number will be different at different time)DISABLE AUTO UPDATE VIA “ABOUT:CONFIG” = “CONFIG-EDITOR” IN THUNDERBIRD/FIREFOX:
Change below preference/options/settings, to disable update or auto-update:
- type
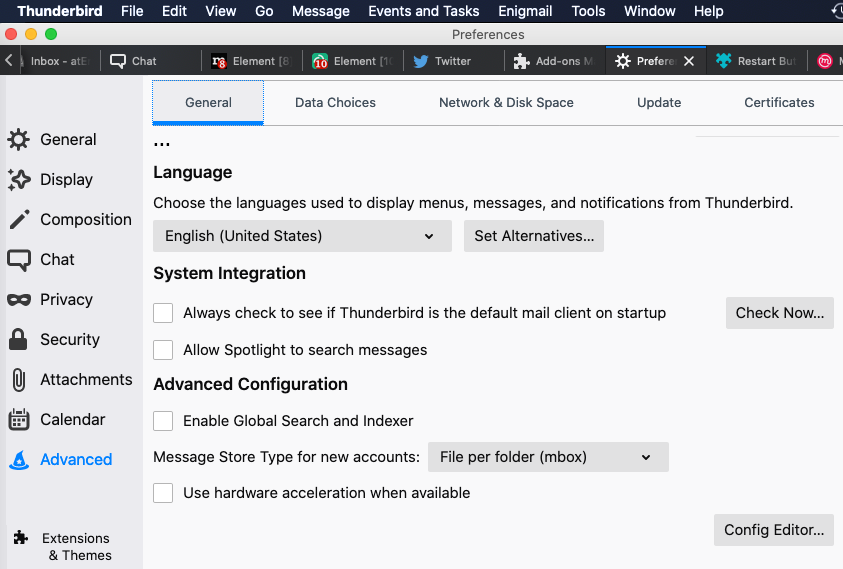
“about:config”(without previous double-quote symbols) in a browser-tab address bar inside Thunderbird/Firefox , then press “Enter“,
- or goto TB main-menu > Tools > Options , or goto TB’s
Preferences/settings , then gotoAdvanced>General> at bottom side you should see"Config Editor".
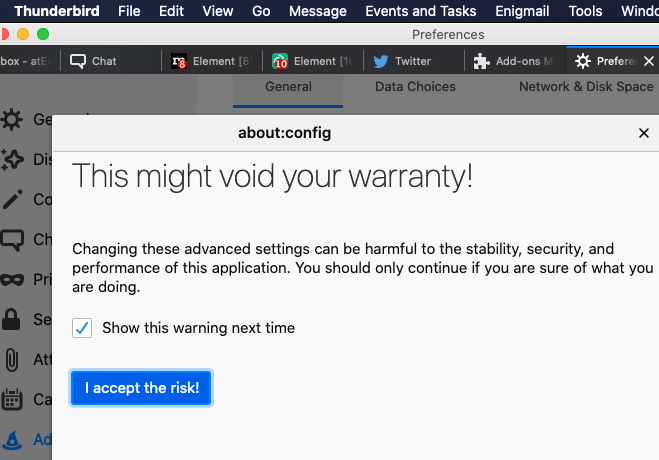
Config-Editor is shown above in bottom-right corner.- you have to agree “I accept the risk!” button shown in below, to proceed into editing stage of preference/setting
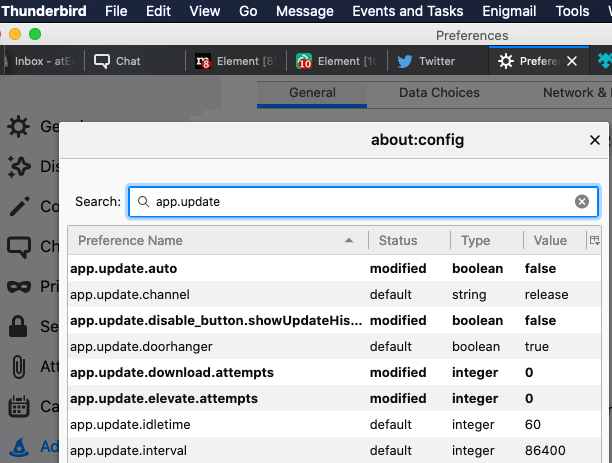
- in search box, type to search for this setting:
“app.update.auto”- double-click on the
“app.update.auto”option to toggle/switch the setting in-between"true"or"false". If it is set to “true“, then automatic updates are enabled . If set to “false“, automatic updates are disabled.
- search for
"app.update.enabled"setting, if exists and if it is not showingfalse, then changetrueby double-clicking on it intofalse, then any update will be disabled.
- You may also create this setting if it does not exist, and then set it to
falseanyway.- when
"app.update.enabled"isfalse(any update is disabled), then TB/FF will also ignore the“app.update.auto”setting/option even if itstrue.- search for
"app.update.silent"setting: if it exists and if you set it totrue, then TB/FF will not show you reminder message when new update is available. If it isfasle, then TB will show you update notification, and you have to choose if you want to update or not.
- this setting should be set to
true, so that TB/FF can atleast notify you when a newer update is available, as some updates are really helpful.- I like this option, as it informs me when a new update available & (new) version number of that. Then i like to Cancel this update notification myself, so i keep at
false. My Mac/PC is not used by anyone else, so there is (almost) no-chance that someone in my side can select such an option to update it. I’m always careful about updating anything.- search for
"app.update.doorhanger"setting: if it exists and if you set it tofalse, then TB/FF will not show you notifying icon or reminder message, even when a new update is available.- if your PC/Mac is used also by someone else, or if there is a chance that you may mistakenly choose “Update” (or you forget to NOT-update), then it is better that you disable all update & notification by doing these: keep
“app.update.auto”atfalse,"app.update.silent"attrue,"app.update.enabled"atfasle,"app.update.doorhanger"atfalse.- WHEN A SETTING DOES NOT PRE-EXIST, THEN HOW DO I ADD IT MANUALLY ? create it manually this way : type any word, for-example “doorhanger” in “Search” box, then right-click on empty area below “Preference Name” column, or right click on the column header “Preference Nane” > popup window will appear, select “New” . As the
"app.update.doorhanger"setting can only have valuefalseortrue, so it is a “Boolean” type setting, so select “New” > “Boolean” , then enter preference name"app.update.doorhanger"> then select “false” or “true” value, based on what YOU want it to perform.- More info:
http://kb.mozillazine.org/About:config_Entries#Update._and_Update_notifications
http://kb.mozillazine.org/Security_PoliciesDISABLE AUTO UPDATE VIA “REGEDIT” IN WINDOWS:
In windows, if you want to make sure, Thunderbird app update is completely disabled, then for both 64bit & 32bit Windows or TB, follow below steps:
- run
regedit.exe, ( reg =registry ) , accept the RISK related warnings, and find/browse to below reg key location:
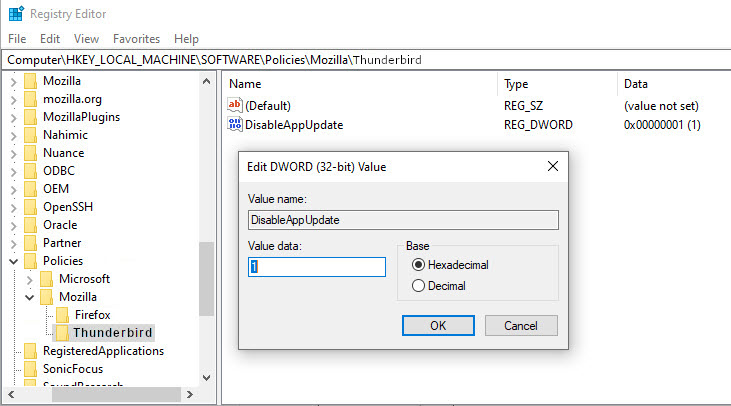
•HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Mozilla\Thunderbird(for Thunderbird=TB).
orHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Thunderbird(for Thunderbird=TB).
•HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Mozilla\Firefox(for Firefox=FF).
- If any one of the above/below (Thunderbird related) reg keys does not exist in Windows Registry, then Create them with a right-click on the previous key (for example: “Mozilla”), and then select
New>Key> specify key name (for example: “Thunderbird” or “Firefox”), then right-click on the keyThunderbirdto configure TB, or, right-click on keyFirefoxto configure FF , and again selectNew>Dword(32-bit) Value > name itDisableAppUpdate> set its value to1to disable TB/FF app update & auto-update.
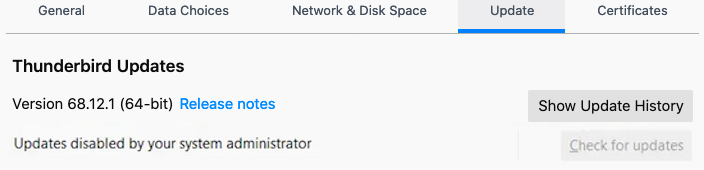
( If later you want-to/need-to enable app update, then you may setDisableAppUpdatekey value to0. )- After above setting is done, user will see a line
“Updates disabled by your system administrator”
has appeared under the version number, in Thunderbird, and such line will also appear in TB main-menu >"About"popup info page, and inside"Update"tab or under"Update"section, etc.
- if you want to disable only AUTO UPDATE (not TB/FF app update/upgrade), then create/goto below reg entry & set your preferred value:
• goto/createHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Mozilla\Thunderbird\AppAutoUpdatefor TB, and set value to0. To enable auto-update use value1.
• goto/createHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Mozilla\Firefox\AppAutoUpdatefor FF, and set value to0. To enable auto-update, use value1.- if you prefer to NOT update extensions/addons, then create this reg entry:
• goto/createHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Mozilla\Thunderbird\ExtensionUpdatefor TB, and set it’s value to0. To allow extnsn/addon update set value to1.
• goto/createHKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Mozilla\Firefox\ExtensionUpdatefor FF, and set it’s value to0. To allow extsn/addon update set value to1.In newer TB versions, above settings may be ignored, and OS other-than Windows-OS does not use Windows-REGISTRY, so, to make sure that update or auto-update is completely disabled in Linux/Unix/macOS, you have to apply POLICY RULE based solution.
TB = Thunderbird . FF = Firefox.
OS = Operating System (for example: Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, Android, iOS, etc).UNHIDE THE HIDDEN FILES/FOLDERS:
Users who can’t view/see the files/folders mentioned in below, those users can use below commands to UNHIDE the HIDDEN files/folders:
• in macOS > start “Finder” app , “Finder” is very similar to Windows-“Explorer” > in Finder, in left side/pane, select “Applications” > then scroll down & go into “Utilities” subfolder > then click on “Terminal” or “Terminal.app” to start it.
• type below command inside “Terminal” ( macOS “Terminal” is like Windows “Command-Prompt”):
defaults write com.apple.Finder AppleShowAllFiles true
• then you must reboot Mac-computer OR run below command:
/usr/bin/sudo /usr/bin/killall Finder /System/Library/CoreServices/Finder.app
or, run just this:/usr/bin/sudo /usr/bin/killall Finder
or, just this:sudo killall Finder
then all hidden files+folders will by-default be shown to user in macOS Finder. )
• in Windows, start/open windows “File Explorer” (aka “Explorer”, aka “Windows Explorer”) from the taskbar , select “View” > “Options” > change folder and search options : select the “View” tab and, in “Advanced” settings, select “Show hidden files, folders, and drives” > and also select “Show File name extensions” > then “OK”.in macOS, inside any file browsing window, user can also press below THREE buttons altogether ONCE, to show HIDDEN files/folders:
[Command⌘] + [Shift⇧] + [.>]
if user press-es above three buttons again, file-browsing-window will HIDE the HIDDEN files/folders.By default in macOS, “Finder” will keep most of the file’s extension hidden . But we need to see all File’s extension, so we can be sure & not make mistake . To view all file’s extension, do below steps:
in macOS > start “Finder” app > goto main menu > Finder > Preferences > Advanced > select"Show All Filename Extensions"option.DISABLE AUTO UPDATE VIA CHANGING THUNDERBIRD UPDATE POLICIES:
For TB/FF version v62 & later, and TB/FF ESR v60 & later, please read essential instruction on policies that any OS user first need-to understand, here.
- Windows – locate the sub-folder where your
"thunderbird.exe"(or"firefox.exe") file is, then create a sub-folder called"distribution"next to the EXE file, then create a file"policies.json"inside the"distribution\"sub-folder.
"thunderbird.exe"file/app is usually located here:
"C:\Program Files\Mozilla Thunderbird\"(if you’re using 64bit edition)
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Thunderbird\"(if you’re using 32bit edition)"firefox.exe"file/app is usually located here:
"C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\"(if you’re using 64bit edition)
"C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\"(if you’re using 32bit edition)- macOS – go inside
"Thunderbird.app", (for which you want to disable update or disable auto-update), by right-clicking on"Thunderbird.app"icon/file, & then select"Show Package Contents"option, create a sub-folder"distribution/"inside the"Resources/"sub-folder, like this:"Thunderbird.app/Contents/Resources/distribution/", then create a file called"policies.json"inside"distribution/"sub-folder.
- go inside
"Firefox.app"(for which you want to disable update or auto-update), by right-clicking on"Firefox.app"icon/file, & then select"Show Package Contents"option, create a sub-folder"distribution/"inside the"Resources/"sub-folder, like this:"Firefox.app/Contents/Resources/distribution/", then create a file called"policies.json"inside"distribution"sub-folder.- Then follow from here: 1, 2.
- Note:
"Thunderbird.app"(or"Firefox.app") is usually located inside the"Applications/"folder, under the"/"root folder of Mac storage drive, here:"/Applications/"- Linux/Unix – create the file
"policies.json"inside"distribution/"folder, located here:"thunderbird/distribution/"for TB, (or create"distribution/"here"firefox/distribution/"for FF), different OS distro (aka: distribution) keeps the thunderbird (or firefox) app folder at different location, for-example: TB may be located here:"/opt/thunderbird/","/usr/local/thunderbird/", etc. Same way, FF could also be in different location in different distro, for example, it can be here:"/opt/firefox/","/usr/local/firefox/", etc.- If you don’t want to create the
"distribution/"sub-folder inside TB/FF app folder, then you can also create or specify a system-wide policy by placing the json file here for TB:/etc/thunderbird/policies/(or place here for FF:/etc/firefox/policies/), in macOS/Linux/Unix.- create a policy rule inside the
"policies.json"file, (as shown inside above linked webpages, and also shown in below code/quote box), to disable auto-update use below policy rule:{ "policies": { "AppAutoUpdate": false } }
- to disable/stop application update completely, use below policy rule:
{ "policies": { "DisableAppUpdate": true } }
- if you use
"DisableAppUpdate"policy rule, then specifying"AppAutoUpdate"is not needed. When"DisableAppUpdate"rule istrue, then auto-update will be automatically disabled (turned-off).- when you will update TB/FF manually or when you will install newer updated TB/FF version manually, then this JSON file will be deleted, so keep a backup somewhere. When you finish update manually, then copy-paste
"policies.json"again inside"distribution/"sub-folder (inside TB/FF app working folder), if you don’t want the newer version to auto-update or update, without your approval or permission.- if you goto “Update” tab or section inside TB settings/Preferences/Options, then you should see info like below:
“Updates disabled by your system administrator”
- to disable extension/addon update, use below policy rule:
{ "policies": { ... "ExtensionUpdate": false ... } }the
...in above is your other policy rules.TB = Thunderbird . FF = Firefox.
DISABLE AUTO UPDATE VIA CHANGING THUNDERBIRD “PREF.JS” CONFIG FILE:
For TB/FF version v62 & earlier, user would need-to & can do these changes:
- if TB/FF is running, then you may/can goto TB main-menu >
Help>Troubleshooting Information> press Ctrl+F to find this word (or to find profile information row), type:about:profiles> click-onabout:profileslink > write down the active Root & Local PROFILE folder/directory path name(s) , they will have the word.defaultat-end (or other PROFILE’s name/word), write it down. If the information row has a[ Browse ]button, then press it to open-up the profile folder quickly, inside your OS’s file-browser software.- close/EXIT from Thunderbird=TB / Firefox=FF, if it is running.
- if you could-not follow the
"Troubleshooting Information"step shown above (to reach the “profile” folder locaiton quickly), then follow these: browse/navigate to the following folder/directory location(s), based on your OS (operating system), to find & open TB/FF"PROFILE"folder/directory:
- Windows XP/Vista/7/8/10 – for TB profile goto
“%APPDATA%\Thunderbird\“(or“%APPDATA%\Mozilla\Thunderbird\“)
or for FF profile goto“%APPDATA%\Mozilla\Firefox\“(or“%APPDATA%\Mozilla\“)
• in newer Windows,“%APPDATA%\“env-var usually points to this folder/directory location:“C:\Users\<WindowsUserName>\AppData\Roaming\“
• in WinXP/2000,"%APPDATA%\"points-to"C:\Documents and Settings\<WindowsUserName>\Application Data\"
•"%APPLOCALDATA%"usually is“C:\Users\<WindowsUserName>\AppData\Local\“(it holds local data, cache data, etc)- Unix/Linux – for TB profile goto
“~/.thunderbird/“, but different Linux/Unix distro (aka: distribution) may use different location, in some distro “profile” may also be here“~/.mozilla-thunderbird-<profile-name>/“
• For FF profile, goto“~/.mozilla/“
• the“~“symbol points-to$HOME/directory/folder, it is usually located here:/Users/<YourLinuxOrUnixUserName>/- macOS X / XI – for TB profile goto
“~/Library/Thunderbird/“or“~/Library/Application Support/Thunderbird/“
• for FF profile goto“~/Library/Application Support/Firefox/“
• the“~“symbol indicating to your$HOME/directory/folder:/Users/<YourMacOSUserName>/- open the
“Profiles”sub-folder, to see all items under it.- then open (aka: go-inside) the sub-folder that represents the “profile” that your TB/FF app is using. Name of this “profile” sub-folder will vary. Usually it begins with a bunch of alpha-numeric characters (often shown as
xxxxxxxx) & followed-by or ends-with“.default”(or otherprofilename).
- if you view files & folders sorted/based on
Date:Modified, and if you go inside each sub-folders under the“Profiles”sub-folder, and if you compare last-modified date of item therein, you can realize which sub-folder was used last time & very recently by the TB/FF app that is the current/last TB/FF that got updated.- open the
prefs.jsfile inside “profile” ("xxxxxxxx.<profile-name>") sub-folder, with a text editor likeNotepad++(win),TextMate(mac),gedit(mac), etc.- find the line inside the
pref.js(“PREF.JS”) file that containsapp.update.enabled, if it doesn’t exist then add a line for it and set it as you want, with any one of the below line (but do-not use both lines):
- automatic update enabled:
user_pref("app.update.enabled", true);- automatic update disabled:
user_pref("app.update.enabled", false);- if you do not want AUTO new updates for Thunderbird (or Firefox) EXTENSIONS (aka: ADDONS), then find/add this
"extensions.update.enabled"setting/preference line, insidepref.jsfile, if it does not already exists, & set it’s value tofalse, as shown in below:
user_pref("extensions.update.enabled", false);- if you do not want to show the
"Show Update History"button, that is shown inside"Update"tab, inside TB’s Preferences / Settings / Options, then add this"disable_button.showUpdateHistory"setting/preference line, insidepref.jsfile if it does not already exists, & set it’s value tofalse, as shown in below:
user_pref("app.update.disable_button.showUpdateHistory", false);- More info:
http://kb.mozillazine.org/Files_and_folders_in_the_profile_%2D_Thunderbird
http://kb.mozillazine.org/Profile_folder_%2D_Thunderbird
http://kb.mozillazine.org/Category%3AProfile_contents_%28Thunderbird%29
http://kb.mozillazine.org/Profile_folder_%2D_Firefox
http://kb.mozillazine.org/User.js_file
http://kb.mozillazine.org/Show_hidden_files_and_foldersTB = Thunderbird . FF = Firefox.
DELETE UPDATE-EXECUTABLE IF IT WAS AUTO-DOWNLOADED BY THUNDERBIRD:
Thunderbird=TB will auto download new updates/executables inside this/these below mentioned sub-folder(s), before you applied above settings, if TB has already obtained update, then remove it with below procedure:
- open file-browser, & browse/go to this sub-folder/directory:
- macOS — check for TB
"updater"file in these folders:"/Users/<YourUserName>/Library/Thunderbird/updates/"
• or check for FF"updater"file in these folders:"/Users/<YourUserName>/Library/Application Support/Mozilla/updates/"- Windows XP,2000,Vista,7,8.1,10 — check for TB
"updater.exe"file inside these folders:“C:\Program Files\Mozilla Thunderbird\“,“C:\Program Files\Mozilla Thunderbird\updates\“,“%APPDATA%\Thunderbird\updates\“
• check for FF"updater.exe"file inside these folders:“C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\“,“C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\updates\“,“%APPDATA%\Mozilla\updates\“,“%APPDATA%\Mozilla\Firefox\updates\“
• If you are using 32bit TB/FF then look additionally also inside this folder:“C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Thunderbird\“(or“C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\“)- Unix/Linux — look for TB “updater” executable file inside these folders:
“~/.thunderbird/updates/“,“~/.mozilla-thunderbird-<profile-name>/updates“
• or look for FF"updater"executable file inside these folders:“~/.mozilla/updates/“or“~/.mozilla/firefox/updates/“- and DELETE below mentioned three files from inside above-mentioned specific
"updates"(or TB/FF app working-directory) sub-folder(s) , especially or atleast the"updater"(in macOS/Linux/Unix) or"updater.exe"(in Windows) executable file.
- these three files are related to update and auto-update:
•update-settings.ini,
•updater.ini,
•updater.exe(Windows) orupdater(macOS/Linux/Unix)- when
“about:config”,pref.js, policies or regkey, etc setting-up step(s) are done, from then-on TB/FF will-not and should-not (automatically) download any new update installer anymore.ADD EXCEPTION RULE INTO UPDATE/VERSION MONITORING APPS:
There are various apps, that can trigger/start/initiate an auto-update process for other apps, (as “updating” techniques/settings are publicly known). Usually these apps obtain version number of your local app(s), in your computer. Then they obtain version number for specific last updated app, either from monitoring app’s own remote web-server, or obtain version number from local app developer’s remote web-server.
So, if you’re using such (monitoring) app(s), then you MUST also have+need to create an EXCEPTION (rule) for Thunderbird (or Firefox) app, inside that/those monitoring app(s), so-that those monitoring apps do-not initiate/trigger an auto-update process.
Example:
- Windows: anti-virus or firewall or security-suite software/tools.
- Linux/Unix app/package update/upgrade/management tool
yumcan update app(s), tool(s), library(s), etc
- add below exclude line(s) into
yumconfig file:/etc/yum.conf
for Thunderbird:
exclude=thunderbird*
for Firefox:
exclude=firefox*How To Get OLDER Thunderbird(TB) or Firefox(FF) Version:
Below sites contain installer program, integrity-code (hash/checksum) files, etc for different versions and for different languages & localities:
- Thunderbird v68.12.1:
https://ftp.mozilla.org/pub/thunderbird/releases/68.12.1/- Thunderbird other versions:
https://archive.mozilla.org/pub/thunderbird/releases/- Thunderbird stable+latest release:
https://www.thunderbird.net/en-US/thunderbird/all/- Firefox (other versions):
https://archive.mozilla.org/pub/firefox/releases/- Firefox v56.0.2 , Firefox ESR v52.9.0.
- Firefox latest+stable version
Portable Editions:
Windows:
- Portable Thunderbird Legacy (v68)
- Portable Thunderbird
- Portable Firefox ESR v52.9.0(Gecko without Servo)
- Portable Firefox v56.0.2(Gecko without Servo)
- Portable Firefox(Gecko with Servo/Quantum)
NOTE:
App’s devs will release various types of updates. Some “update” are mainly feature related update (feature addition, removal, fix, patch, update, etc), some “update” are mainly app’s security related update (security enhancement, improvement, patch, bugfix, etc), etc, etc.
USER / YOU NEED TO INSTALL THE SECURITY RELATED UPDATES, ATLEAST,
as it secures your computer thus in-turn it secures your/user’s safety,
provided that, you/user can trust app’s devs, that they/devs will release update that is/are actually beneficial for app’s USER / YOU, and does not violate/abuse your or any other user’s any human-rights.0There is one more useful option in policies.json file –
ManualAppUpdateOnly. Like"DisableAppUpdate": trueit allows to disable automatic updates and all annoying “Update available” notifications. And at the same time it still allows to update Thunderbird/Firefox manually through “About Firefox” menu when it is necessary.The description from mozilla documentation (https://github.com/mozilla/policy-templates/blob/master/README.md#manualappupdateonly)
Switch to manual updates only.
If this policy is enabled:
- The user will never be prompted to install updates
- Firefox will not check for updates in the background, though it will check automatically when an update UI is displayed (such as the one in the About dialog). This check will be used to show “Update to version X” in the UI, but will not automatically download the update or prompt the user to update in any other way.
- The update UI will work as expected, unlike when using DisableAppUpdate.
Example of
policies.json:{ "policies": { "ManualAppUpdateOnly": true } }See outstanding answer from @atErik for details how to install this file – https://stackoverflow.com/a/64980413/8996217
This option works since Firefox 87 (and since Thunderbird 87 likely) so it would not help with Thunderbird 68 though. Anyway I believe it should be mentioned for completeness
Source: settings – How to disable Thunderbird AUTO UPDATE – Stack Overflow
MYSQL Table Sizes
Table size for all databases:
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS `Database`, TABLE_NAME AS `Table`, ROUND((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES ORDER BY (DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) DESC;
Table sizes for a single database:
SELECT TABLE_NAME AS `Table`, ROUND(((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024), 2) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE table_schema = "<database name>" ORDER BY (data_length + index_length) DESC;
Size of a single database:
SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA AS `Database`, ROUND(SUM(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024, 2) AS `Size (MB)` FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA="<database name>";


Dec 25, 2020 at 21:54
Dec 26, 2020 at 2:52
Dec 28, 2020 at 2:33
Jan 1, 2021 at 3:27
Apr 6, 2021 at 13:15