Source: Coalition Partners | MRSC
All posts by smarc
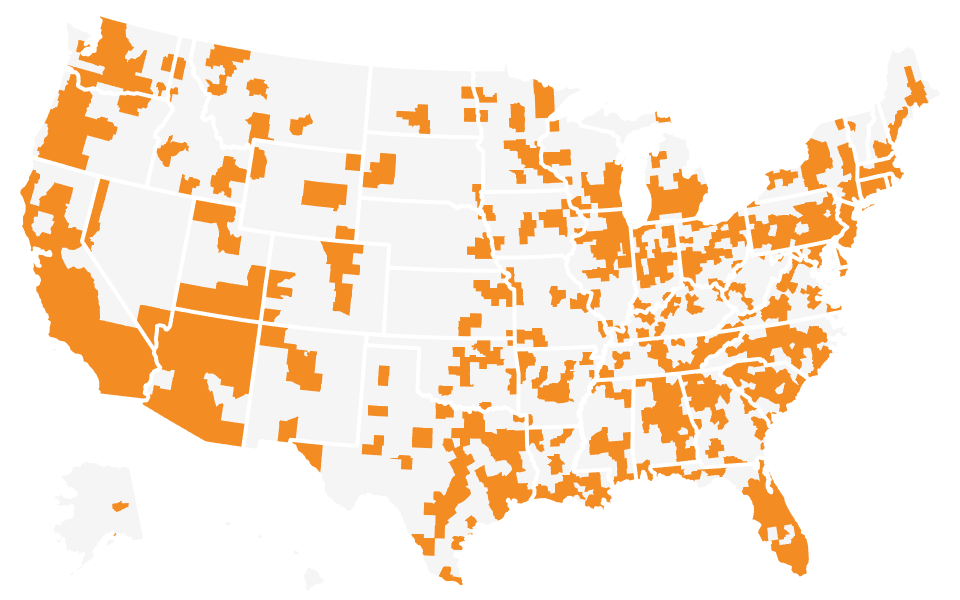
Project Sunroof
Enter a state, county, city, or zip code to see a solar estimate for the area, based on the amount of usable sunlight and roof space.
Source: Project Sunroof
Installing MS Office Group Policy Administrative Templates (ADMX) | Windows OS Hub
You can use Microsoft Office administrative templates (ADMX) to centrally manage the settings of MS Office programs (Word, Excel. Outlook, Visio, PowerPoint, etc.) in the Active Directory domain using Group…
Source: Installing MS Office Group Policy Administrative Templates (ADMX) | Windows OS Hub
How to Hide or Show User Accounts from Login Screen on Windows | Windows OS Hub
How to Hide or Show User Accounts from Login Screen on Windows
By default, the Windows login screen displays the account of the last user who logged on to this computer and a list of all local users. Windows allows you to hide or show the last signed-in user name, or even list all local or active domain users on the computer sign-in screen.
Contents:
Hide Last Signed-in Username from Windows Login Screen
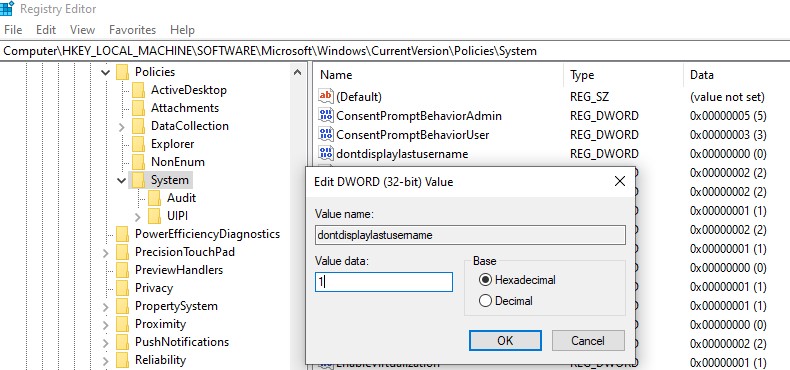
Users find it convenient to see the last logged account name on the Windows Logon Screen without having to type it in manually each time. For security reasons, you can prevent the last username from being displayed on the Windows logon screen on public computers (or other insecure locations) by using GPO:
- Open the domain (
gpmc.msc) or local Group Policy editor (gpedit.msc) and go Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options;- Enable the policy Interactive logon: Don’t display last signed-in. This policy is disabled by default;
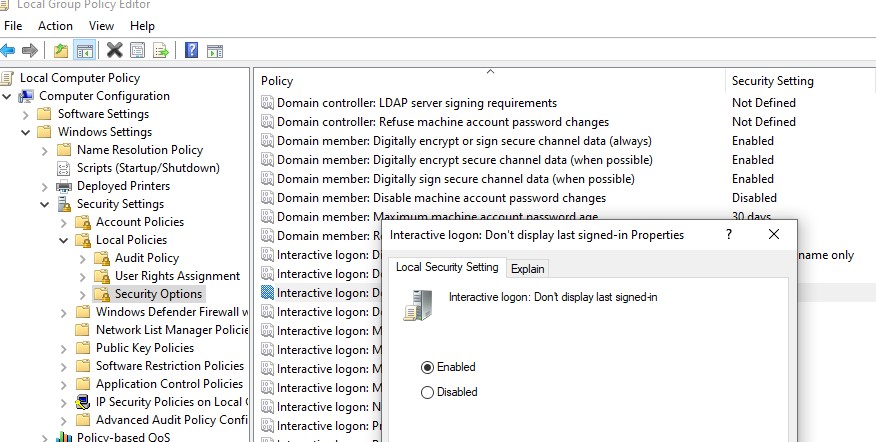
- To hide the logged-in username on the lock screen (when the computer is locked by pressing
Win+Lor through the lock screen GPO), enable the Group Policy option “Interactive logon: Display user information when the session is locked” and set the value “Do not display user information”.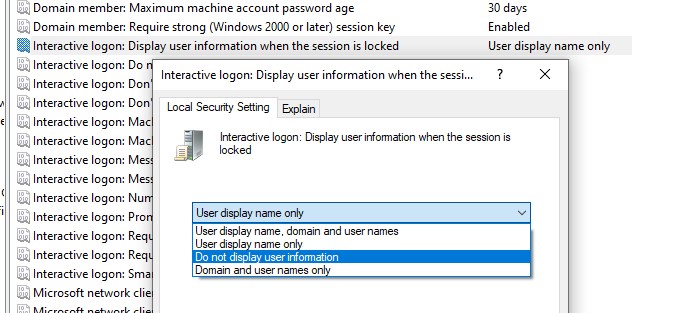 The registry parameter DontDisplayLockedUserId in the same registry key with a value of 3 matches this policy setting.
The registry parameter DontDisplayLockedUserId in the same registry key with a value of 3 matches this policy setting.Blank username and password fields now appear on the Windows logon and lock screens instead of the previously signed-in username.
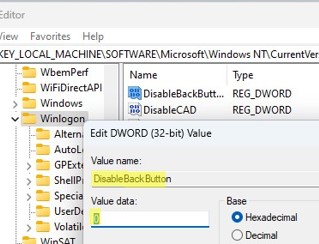
You can hide the list of users from the Windows lock screen by using the DisableBackButton registry parameter:
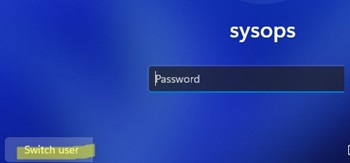
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" /t REG_DWORD /f /d 0 /v DisableBackButtonTo unlock the computer, the user must enter their password. To view a list of local user accounts, the user must first press the Switch User button on the lock screen.
Show All Local Users on the Windows Sign-in Screen
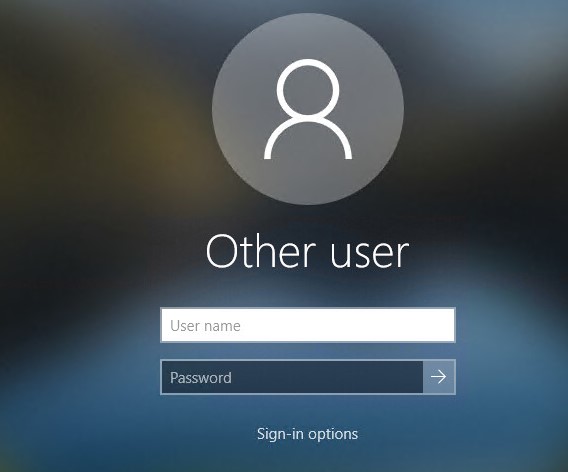
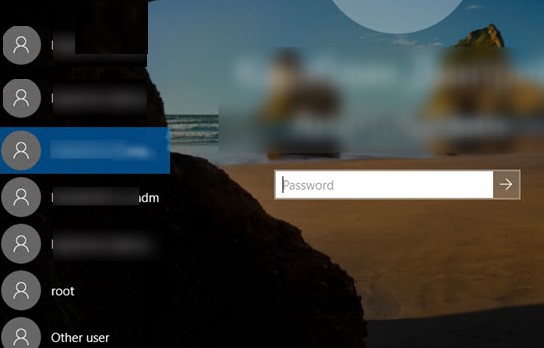
By default, modern Windows builds (tested on Windows 11 23H2 and Windows 10 22H2) always show a list of enabled local users in the bottom left corner of the login screen. This only works on computers that are not joined to the Active Directory domain. Hidden (see below) and disabled user accounts are not displayed on the sign-in screen.
To log on to the computer, the user simply clicks on the required user account and enters its password.
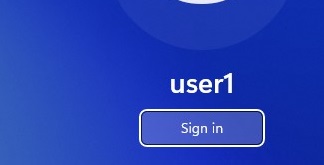
If there is no password set for the user account (blank password), simply select a user and click the Sign-In button to automatically log on to Windows without a password.If the list of local users is not displayed on the Windows logon screen, check the following settings in the Local GPO editor (
gpedit.msc):
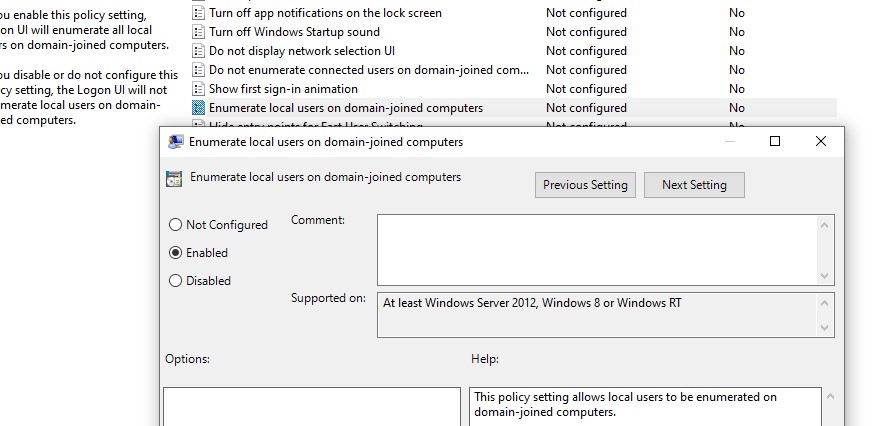
- Interactive Logon: Do not display last signed-in =
Disabled(Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options);- Enumerate local users on domain-joined computers =
Enabled(Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Logon).Restart your computer to apply the new Group Policy settings.
Show Logged In Domain Users on Windows Logon Screen
If more than one user is using the same computer, you can see a list of users with active sessions on the Windows sign-in screen. An active session means that the user is logged on to the computer. This can be a shared computer (used in user switching mode), a kiosk, Windows Server hosts running the RDS role, or Windows 11/10 devices that allow multiple RDP connections).
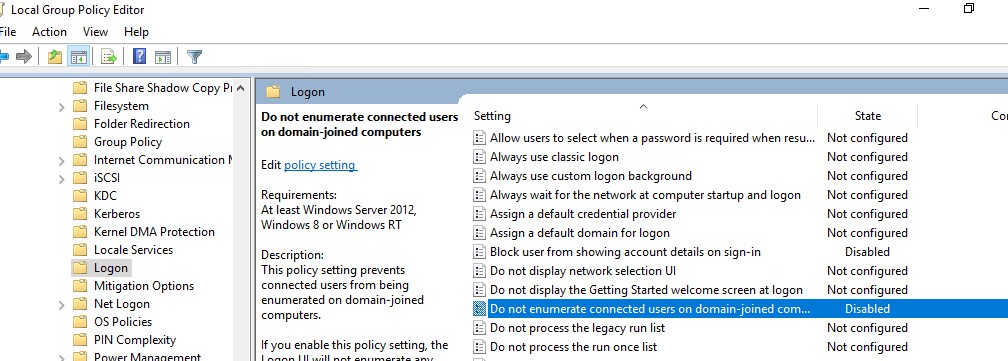
Check that the following policies are disabled in Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies -> Security Options:
- Interactive logon: Don’t display last signed-in: Disabled
- Interactive logon: Don’t display username at sign-in: Disabled
Then disable the GPO options in Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Logon:
- Block user from showing account details on sign-in: Disabled
- Do not enumerate connected users on domain-joined computer: Disabled
On a domain-joined computer, you can check the resulting settings of these GPO options using thersop.mscor gpresult.A list of logged-in users will then appear on the Windows Welcome Screen. Both active and disconnected user sessions (for example, due to RDP timeout) are displayed.
You can display Active Directory user profile photos on the Windows logon screen instead of the default user icons.Hide Specific User Accounts from the Windows Sign-in Screen
The Windows Welcome screen always displays users who are members of one of the following local groups: Administrators, Users, Power Users, and Guests (except the disabled user accounts).
You can hide specific users from the list on the Windows login screen through the registry. For each user you want to hide, create a DWORD parameter under the reg key
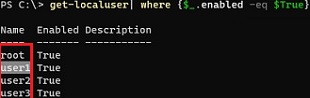
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\SpecialAccounts\UserListwith the username and value 0.List all local user account names using PowerShell or cmd:
Get-LocalUser | where {$_.enabled –eq $true}Or:
Net userTo hide a specific user account (for example, user123) from the Windows sign-in screen, run the command:
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\SpecialAccounts\UserList" /t REG_DWORD /f /d 0 /v User123If you want to show the hidden user on the login screen, remove this registry entry or change its value to 1.If the built-in Windows Administrator account is enabled, and it is not the only account with local administrator permissions on the computer (!!!), you can also hide it:
reg add "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\SpecialAccounts\UserList" /t REG_DWORD /f /d 0 /v administratorTo hide all users except the last logged-on user, set the following GPO settings in Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Logon:
- Enumerate local users on domain-joined computers = Disabled
- Do not enumerate connected users on domain-joined computer = Enabled
Source: How to Hide or Show User Accounts from Login Screen on Windows | Windows OS Hub
Ansible Resources
Setting up Vim for YAML editing
Setting up Vim for YAML editing
In this blog post I’m going to show how to set up Vim for easier YAML editing.
You can scroll down to the end for a summary of all installed plugins and config file changes.
Syntax Highlighting
There’s not much to do here. VIM has YAML syntax highlighting built-in and it’s great.
A few years back YAML highlighting in Vim was very slow, and there was often a noticeable lag when opening large files. The workaround was to use the vim-yaml plugin for fast syntax highlighting.
I decided to make a performance benchmark. I loaded up a large YAML file (6100 lines) and compared the time:
# default syntax highlighting
$ vim gen-istio-cluster.yaml --startuptime default.log
$ tail -1 default.log
055.563
# vim-yaml plugin
$ vim gen-istio-cluster.yaml --startuptime vimyaml.log
$ tail -1 vimyaml.log
060.320
As we can see the default syntax highlighting is just as fast as the plugin and there’s no need to install a separate plugin to fix the slow syntax highlighting anymore.
Indentation
Indentation probably the most annoying part about editing YAML files. Large documents with deeply nested blocks are often hard to track and errors are easily made.
YAML documents are required to have a 2 space indentation. However, Vim does not set this by default but it’s an easy fix by putting the following line in the vim config:
autocmd FileType yaml setlocal ts=2 sts=2 sw=2 expandtab
We can also setup Indentation guides. Indentation guides are thin vertical lines at each indentation level and useful to help line up nested YAML blocks.
We can display those lines by using the indentLine plugin. I’ve modified the indentation character to display a thinner line (default is “¦”):
let g:indentLine_char = '⦙'
The result should look like this:
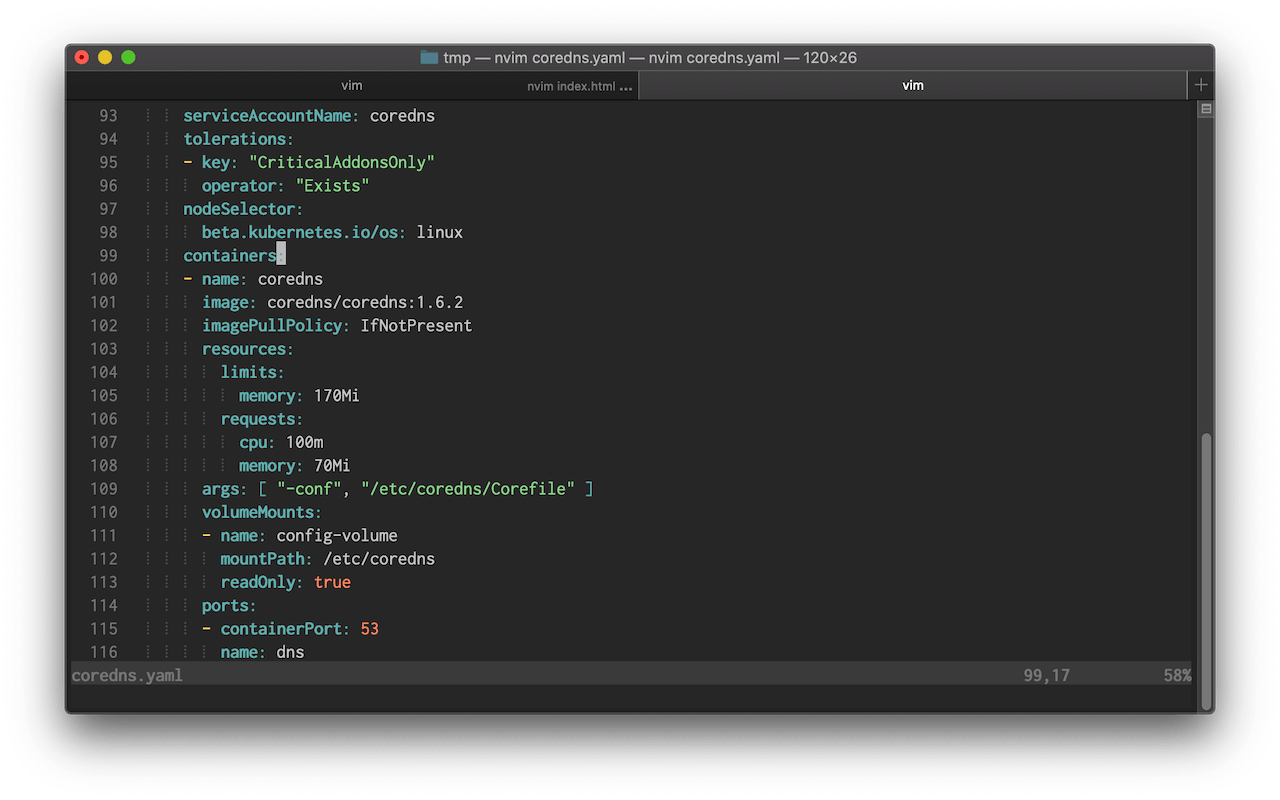
Folding
With folding we can hide parts of the file that are not relevant to our current task.
Vim has built-in support for folding based on the indentation level but the default folding rules make it hard to tell what is folded. This is because the folding starts on the line following the start of a block. To change this we can install the vim-yaml-folds plugin.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison of the default folding (left) compared to vim-yaml-folds (right):
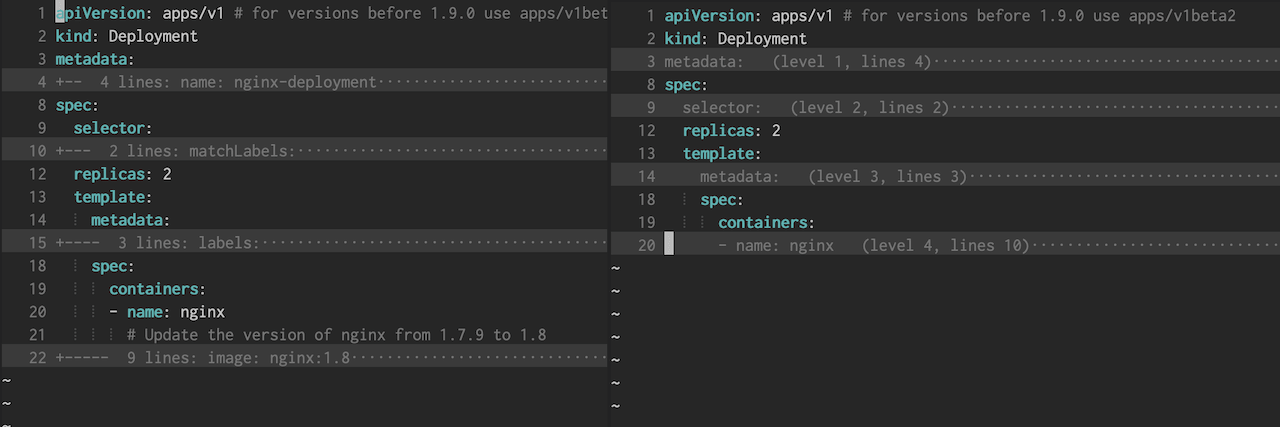
To work with folding we need to remember a few keyboard commands. Vimcasts has a great episode on this here. Most of the time I use the following commands:
- za: Toggle current fold
- zR: Expand all folds
After the plugin is installed and folding is enabled the default settings will fold all blocks by default. To start with unfolded content we can set:
set foldlevelstart=20
There’s also a plugin called restore_view which will save the folds for each file. But be aware that this plugin will create an extra file with folding information for each opened document.
Linting
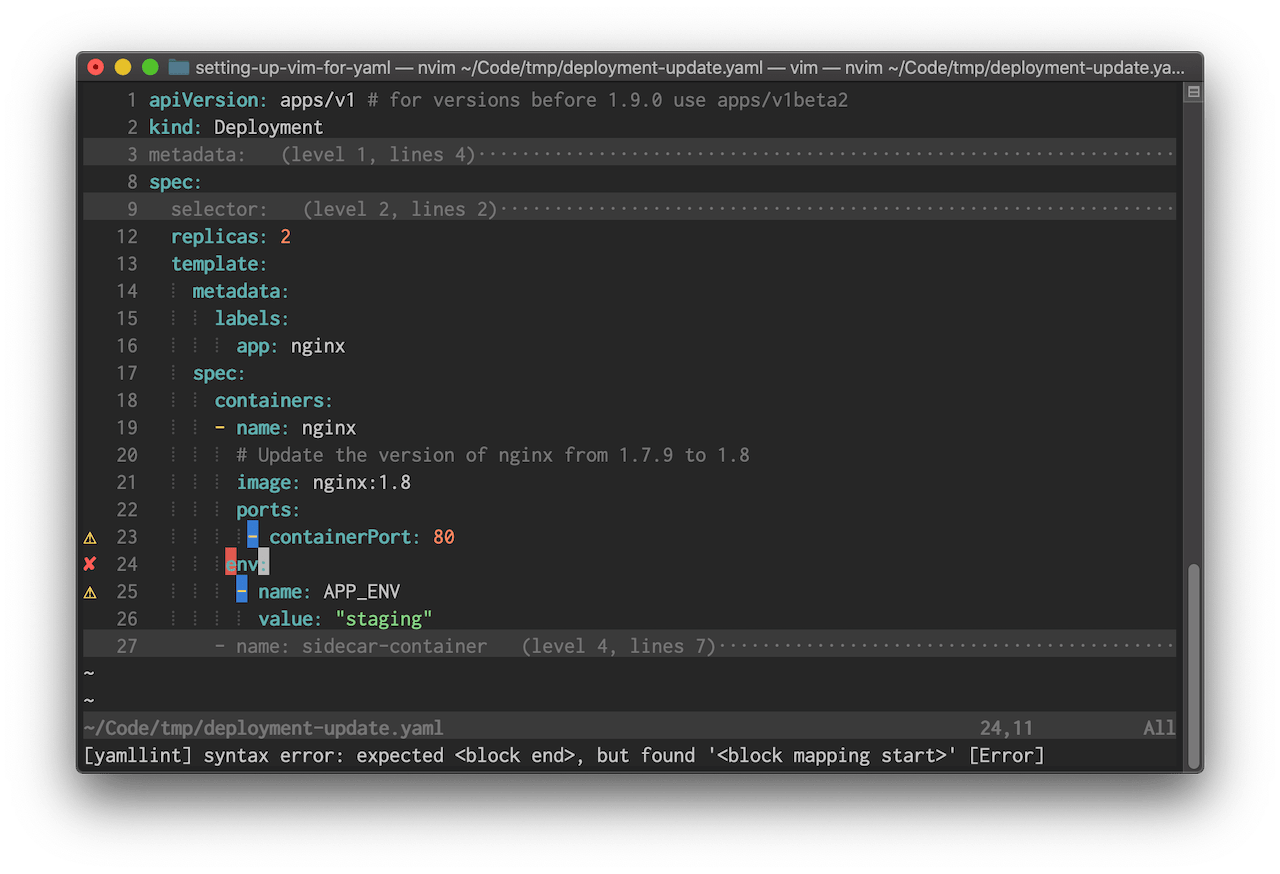
Linting will analyze the code and show any potential errors while we’re writing it which helps us catch formatting or syntax errors early on.
To do this in Vim we can use ALE, an asynchronous linting framework that has support for many languages and tools including YAML. To enable YAML linting in ALE we have to install yamllint, a Python-based YAML linter.
Installation instructions are here. On macOS we can install it with Homebrew:
$ brew install yamllint
The default configuration is fairly strict and shows errors in document style such as line length, trailing spaces or comment indentation.
We can modify the configuration to be less strict. Yamllint already comes with a relaxed version of the default config that is a good starting point. The only additional thing I’ve decided to disable is line length checking.
To do this we open up ~/.config/yamllint/config and paste the following:
extends: relaxed
rules:
line-length: disable
I’ve modified the ALE configuration to change the message format, error symbols and only lint when the file is saved:
let g:ale_echo_msg_format = '[%linter%] %s [%severity%]'
let g:ale_sign_error = '✘'
let g:ale_sign_warning = '⚠'
let g:ale_lint_on_text_changed = 'never'
We can see the errors and warnings on the left side:

Summary
Here’s a summary of the plugins, applications and config modifications:
Vim Plugins
Applications
Config
In ~/.vimrc or ~/.config/nvim/init.vim
autocmd FileType yaml setlocal ts=2 sts=2 sw=2 expandtab
set foldlevelstart=20
let g:ale_echo_msg_format = '[%linter%] %s [%severity%]'
let g:ale_sign_error = '✘'
let g:ale_sign_warning = '⚠'
let g:ale_lint_on_text_changed = 'never'
In ~/.config/yamllint/config
extends: relaxed
rules:
line-length: disableSource: Setting up Vim for YAML editing
How to Change Window Border Settings on Windows 11 [Color, Size]
How do I change the window border size on Windows 11?
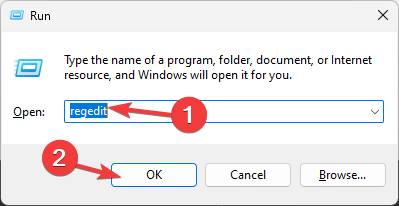
- Press Windows +R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type regedit and click OK to open Registry Editor.
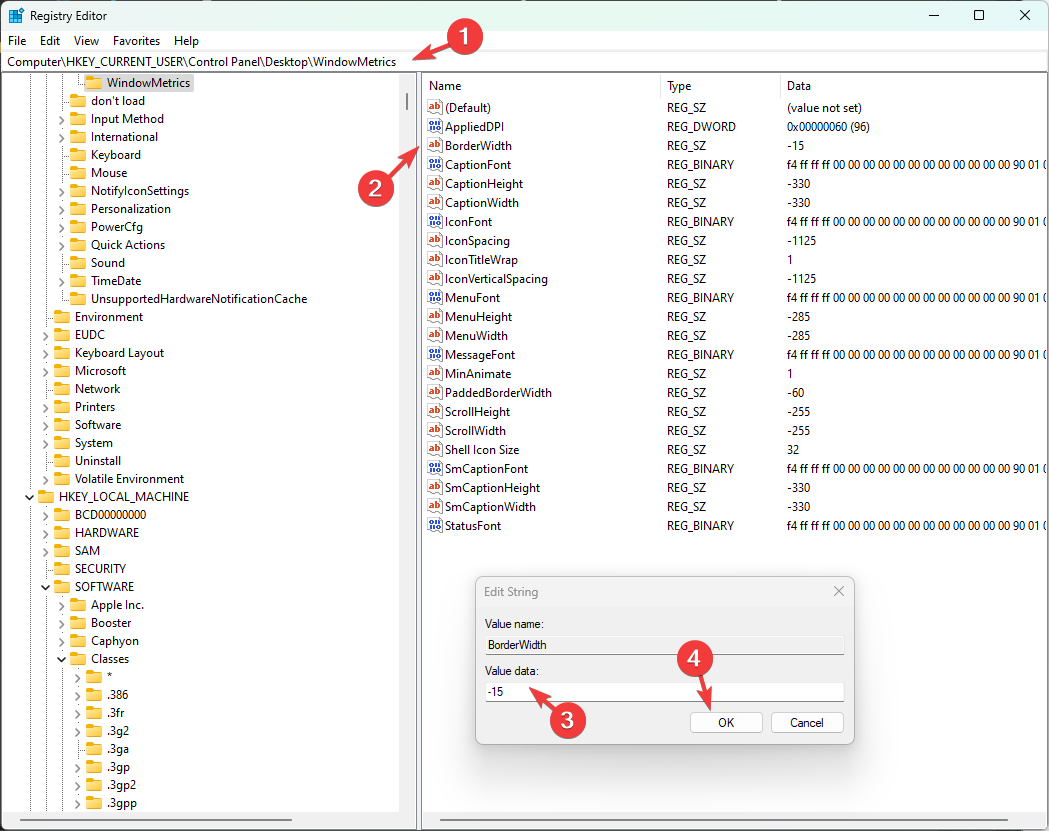
- Navigate to this path:
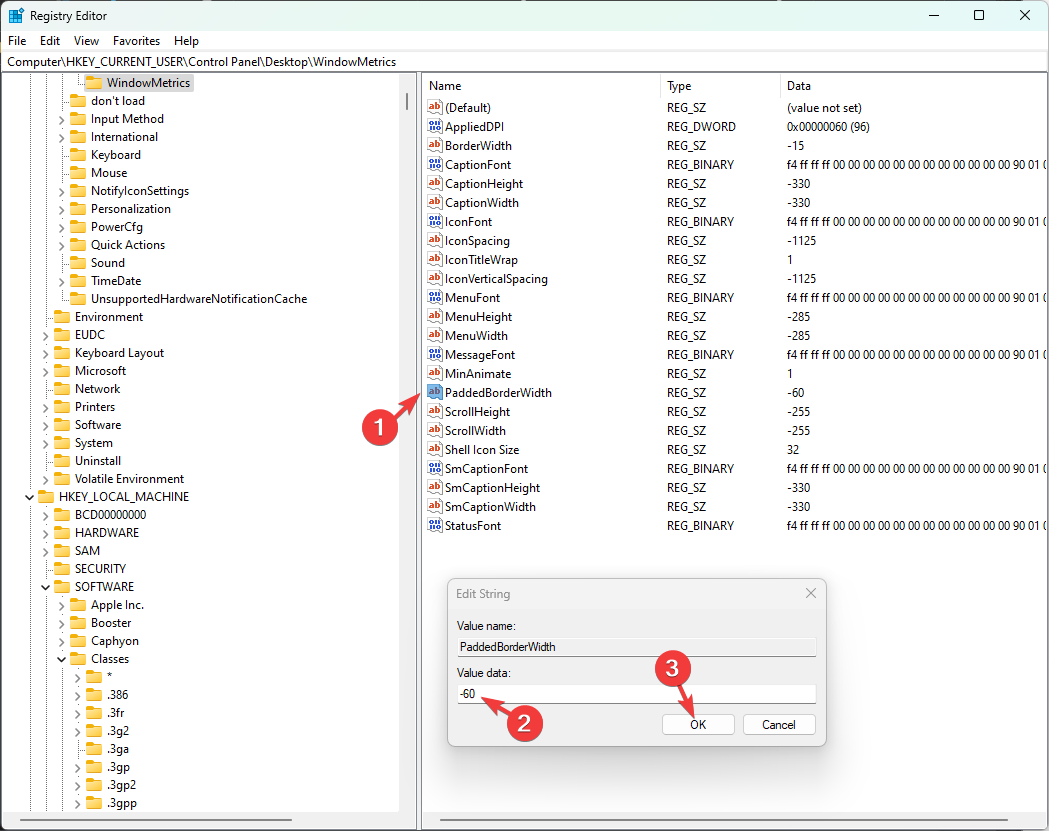
Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Control Panel\Desktop\WindowMetrics- Locate the Border Width option from the right pane and double-click to open it.
- Change the Value data to any value between 0 to -750, then click OK.
- Now locate PaddedBorderWidth, double-click it, change the Value data to 0, then click OK.
- Close Registry Editor and restart your computer to change the border thickness.
Other Windows 11 Changes to Windows Border
- Rounded corners – Windows 11 introduced rounded corners for all windows, including the title bar and borders, giving the OS a cohesive look.
- New accent color feature– Customize the color of the border and title bars irrespective of the theme selected; launch Settings>Personalization>Colors, then Accent color and choose a color.
- Dark Themes – This can be applied to the entire system; for that, press Windows + I to open Settings>Personalization>Colors, locate Choose your mode, & select Dark on drop-down.
- Light Theme – Choose a light theme for the entire system; for that, open Settings>Personalization>Colors, then Choose your mode, and select Light on the drop-down menu.
- Colors on Title Bar – Open Settings>Personalization>Colors, then switch the toggle on for the Show accent color on title bars and windows borders option, then select a color from the palette.
How do I remove window borders in Windows 11?
To disable window border color on Windows 11, all you need to do is switch off the toggle next to the Show accent color on title bars and windows borders in the Settings app.
Source: How to Change Window Border Settings on Windows 11 [Color, Size]
DDC/CI monitor control on Linux
DDC/CI is a set of protocols for controlling monitor features like brightness, contrast, color temperature, input source, … over the display cable (VGA, DVI, HDMI, Display port, …).
The protocol is fairly old (1998) and nowadays most devices support it.
I’m currently using it to:
- Adjust the brightness of my two monitors depending on my room lighting.
- Switch the input source of my monitors for different devices (my laptop, a tower PC and a virtual machine with dedicated GPU). The big advantage here is that you don’t need to buy an expensive KVM switch to support 4K displays / high refresh rates.
How
Required packages
You must install the
ddcutilpackage for your Linux distribution. The official website contains extensive information for troubleshooting.Kernel modules
Ddcutil connects to your screen over an I2C connection, and requires the
i2c-devkernel module to be loaded.You can load the module at runtime using
sudo modprobe i2c-dev.To make it persistent across reboots, you need to add the module to
/etc/modules-load.d/i2c-dev.conf:i2c-devOnce the module is loaded, some files should appear in
/dev/i2c-*.Allow the user to use DDC
By default the i2c dev files are owned by root, preventing other users to control them. One solution to allow your user to control DDC without using
sudois to add a custom udev rule:
/etc/udev/rules.d/99-ddcutil-i2c.rulesKERNEL=="i2c-[0-9]*", GROUP="your-user", MODE="0660", PROGRAM="/usr/bin/ddcutil --bus=%n getvcp 0x10"This rule automatically detects which i2c devices are DDC-capable, and allows members of the group “your-user” to control the file.
You can reload udev rules without rebooting by executing
sudo udevadm triggerIf you have multiple users, you can create a new group and add your user to the group:
groupadd ddc usermod -aG ddc $USERNote:
ddcutil --bus=%n getvcp 0x10is used to get the current brightness of the monitor. This only work with the assumption that all monitors supporting DDC/CI control can be queried for their brightness, which is likely to be true for the immense majority of them.Identify your monitor info
How to address your monitor
The following command queries general information on your connected displays:
ddcutil detect # You should see entries like: # Display 1 # I2C bus: /dev/i2c-0 # EDID synopsis: # Mfg id: DEL # Model: DELL U2419H # Serial number: 833L1N6 # Manufacture year: 2018 # EDID version: 1.4 # VCP version: 2.1There are multiple methods to address your monitor:
- By display number using
--display- By model name using
--model- By serial number using
--sn- By i2c bus ID using
--busThe bus ID method is way faster than the others, but may be unreliable if your hardware changes often.
Which features can be controlled
The following command queries which display features can be get/set for a given monitor:
ddcutil capabilities --bus=0 # You should see something like: # MCCS version: 2.1 # Commands: # Command: 01 (VCP Request) # Command: 02 (VCP Response) # Command: 03 (VCP Set) # Command: 07 (Timing Request) # Command: 0c (Save Settings) # Command: e3 (Capabilities Reply) # Command: f3 (Capabilities Request) # VCP Features: # Feature: 10 (Luminosity) # Feature: 12 (Contrast) # Feature: 14 (Select color preset) # Values: # 04: 5000 K # 05: 6500 K # 06: 7500 K # 08: 9300 K # 09: 10000 K # 0b: User 1 # 0c: User 2 # Feature: 16 (Video gain: Red) # Feature: 18 (Video gain: Green) # Feature: 1A (Video gain: Blue) # Feature: 60 (Input Source) # Values: # 0f: DisplayPort-1 # 11: HDMI-1 # Feature: AA (Screen Orientation) # Values: # 01: 0 degrees # 02: 90 degrees # 03: 180 degrees # 04: 270 degreesYou can get/set those features using:
- Get:
ddcutil --bus=0 getvcp $FEAT_ID- Set:
ddcutil --bus=0 setvcp $FEAT_ID $VALUEScript examples
Change brightness
ddc-setbrightness#!/bin/bash # Usage: ddc-setbrightness 50 ddcutil --bus=0 setvcp 10 "$1" & ddcutil --bus=1 setvcp 10 "$1" & waitSince DDC commands can be slow to execute (especially without
--busaddressing), it is best to run them in parallel and wait for completion.Switch input sources
Very useful when you need to change input sources very often, and don’t have a dedicated button on the monitor (or for automating it).
ddc-switch-inputs#!/bin/bash # Usage: ddc-switch-inputs 1 case "$1" in 1 ) # Config 1: Main PC OUT=("0x0f" "0x20") ;; 2 ) # Config 2: Virtual machine OUT=("0x11" "0x21") ;; * ) echo "Unknown input '$1'" exit 1 ;; esac ddcutil --bus=0 setvcp 60 ${OUT[0]} & ddcutil --bus=1 setvcp 60 ${OUT[1]} & waitReduce eyestrain
ddc-daylight#!/bin/bash # Usage: ddc-daylight night case "$1" in "day" ) BRIGHTNESS=100 TEMPERATURE=0x09 ;; "evening" | "morning" ) BRIGHTNESS=60 TEMPERATURE=0x06 ;; "night" ) BRIGHTNESS=30 TEMPERATURE=0x04 ;; "dark" ) BRIGHTNESS=0 TEMPERATURE=0x04 ;; * ) echo "Unknown time of day '$1'" exit 1 ;; esac ddcutil --bus=0 setvcp 10 $BRIGHTNESS & ddcutil --bus=1 setvcp 10 $BRIGHTNESS & ddcutil --bus=0 setvcp 14 $TEMPERATURE & ddcutil --bus=1 setvcp 14 $TEMPERATURE & wait
Updates:
2022-01-13: Replacedi2c-[0-9]+withi2c-[0-9]*since udev doesn’t support the+extension. Thanks Hendrik W. !
Source: DDC/CI monitor control on Linux
Static Site Generators
Source: Static Site Generators
Static Site Generators – Top Open Source SSGs | Jamstack
Check out this showcase of some of the best, open source static site generators. This is community-drive so be sure to submit your favorite today!
Source: Static Site Generators – Top Open Source SSGs | Jamstack