Sysinternals Utilities Index
Sysinternals Suite
The entire set of Sysinternals Utilities rolled up into a single download.
Sysinternals Suite for Nano Server
Sysinternals Utilities for Nano Server in a single download.
Sysinternals Suite for ARM64
Sysinternals Utilities for ARM64 in a single download.
AccessChk
v6.20 (November 19, 2017)
AccessChk is a command-line tool for viewing the effective permissions on files, registry keys, services, processes, kernel objects, and more.
AccessEnum
v1.32 (November 1, 2006)
This simple yet powerful security tool shows you who has what access to directories, files and Registry keys on your systems. Use it to find holes in your permissions.
AdExplorer
v1.44 (November 15, 2012)
Active Directory Explorer is an advanced Active Directory (AD) viewer and editor.
AdInsight
v1.2 (October 26, 2015)
An LDAP (Light-weight Directory Access Protocol) real-time monitoring tool aimed at troubleshooting Active Directory client applications.
AdRestore
v1.1 (November 1, 2006)
Undelete Server 2003 Active Directory objects.
Autologon
v3.10 (August 29, 2016)
Bypass password screen during logon.
Autoruns
v13.98 (June 24, 2020)
See what programs are configured to startup automatically when your system boots and you login. Autoruns also shows you the full list of Registry and file locations where applications can configure auto-start settings.
BgInfo
v4.26 (October 19, 2018)
This fully-configurable program automatically generates desktop backgrounds that include important information about the system including IP addresses, computer name, network adapters, and more.
BlueScreen
v3.2 (November 1, 2006)
This screen saver not only accurately simulates Blue Screens, but simulated reboots as well (complete with CHKDSK), and works on Windows NT 4, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Server 2003 and Windows 95 and 98.
CacheSet
v1.0 (November 1, 2006)
CacheSet is a program that allows you to control the Cache Manager’s working set size using functions provided by NT. It’s compatible with all versions of NT.
ClockRes
v2.1 (July 4, 2016)
View the resolution of the system clock, which is also the maximum timer resolution.
Contig
v1.8 (July 4, 2016)
Wish you could quickly defragment your frequently used files? Use Contig to optimize individual files, or to create new files that are contiguous.
Coreinfo
v3.31 (August 18, 2014)
Coreinfo is a new command-line utility that shows you the mapping between logical processors and the physical processor, NUMA node, and socket on which they reside, as well as the cache’s assigned to each logical processor.
Ctrl2cap
v2.0 (November 1, 2006)
This is a kernel-mode driver that demonstrates keyboard input filtering just above the keyboard class driver in order to turn caps-locks into control keys. Filtering at this level allows conversion and hiding of keys before NT even “sees” them. Ctrl2cap also shows how to use NtDisplayString() to print messages to the initialization blue-screen.
DebugView
v4.90 (April 23, 2019)
Another first from Sysinternals: This program intercepts calls made to DbgPrint by device drivers and OutputDebugString made by Win32 programs. It allows for viewing and recording of debug session output on your local machine or across the Internet without an active debugger.
Desktops
v2.0 (October 17, 2012)
This new utility enables you to create up to four virtual desktops and to use a tray interface or hotkeys to preview what’s on each desktop and easily switch between them.
Disk2vhd
v2.01 (January 21, 2014)
Disk2vhd simplifies the migration of physical systems into virtual machines (p2v.md).
DiskExt
v1.2 (July 4, 2016)
Display volume disk-mappings.
Diskmon
v2.01 (November 1, 2006)
This utility captures all hard disk activity or acts like a software disk activity light in your system tray.
DiskView
v2.4 (March 25, 2010.md)
Graphical disk sector utility.
Disk Usage (DU.md)
v1.61 (February 13, 2018)
View disk usage by directory.
EFSDump
v1.02 (November 1, 2006)
View information for encrypted files.
FindLinks
v1.1 (July 4, 2016)
FindLinks reports the file index and any hard links (alternate file paths on the same volume.md) that exist for the specified file. A file’s data remains allocated so long as at it has at least one file name referencing it.
Handle
v4.22 (June 14, 2019)
This handy command-line utility will show you what files are open by which processes, and much more.
Hex2dec
v1.1 (July 4, 2016)
Convert hex numbers to decimal and vice versa.
Junction
v1.07 (July 4, 2016)
Create Win2K NTFS symbolic links.
LDMDump
v1.02 (November 1, 2006)
Dump the contents of the Logical Disk Manager’s on-disk database, which describes the partitioning of Windows 2000 Dynamic disks.
ListDLLs
v3.2 (July 4, 2016)
List all the DLLs that are currently loaded, including where they are loaded and their version numbers.
LiveKd
v5.62 (May 16, 2017)
Use Microsoft kernel debuggers to examine a live system.
LoadOrder
v1.01 (July 4, 2016)
See the order in which devices are loaded on your WinNT/2K system.
LogonSessions
v1.4 (July 4, 2016)
List the active logon sessions on a system.
MoveFile
v1.01 (January 24, 2013)
Allows you to schedule move and delete commands for the next reboot.
NotMyFault
v4.01 (November 18, 2016)
Notmyfault is a tool that you can use to crash, hang, and cause kernel memory leaks on your Windows system.
NTFSInfo
v1.2 (July 4, 2016)
Use NTFSInfo to see detailed information about NTFS volumes, including the size and location of the Master File Table (MFT) and MFT-zone, as well as the sizes of the NTFS meta-data files.
PendMoves
v1.2 (February 5, 2013)
Enumerate the list of file rename and delete commands that will be executed the next boot.
PipeList
v1.02 (July 4, 2016)
Displays the named pipes on your system, including the number of maximum instances and active instances for each pipe.
PortMon
v3.03 (January 12, 2012)
Monitor serial and parallel port activity with this advanced monitoring tool. It knows about all standard serial and parallel IOCTLs and even shows you a portion of the data being sent and received. Version 3.x has powerful new UI enhancements and advanced filtering capabilities.
ProcDump
v10.0 (September 17, 2020)
This command-line utility is aimed at capturing process dumps of otherwise difficult to isolate and reproduce CPU spikes. It also serves as a general process dump creation utility and can also monitor and generate process dumps when a process has a hung window or unhandled exception.
Process Explorer
v16.32 (April 28, 2020)
Find out what files, registry keys and other objects processes have open, which DLLs they have loaded, and more. This uniquely powerful utility will even show you who owns each process.
Process Monitor
v3.60 (September 17, 2020)
Monitor file system, Registry, process, thread and DLL activity in real-time.
PsExec
v2.2 (June 29, 2016)
Execute processes on remote systems.
PsFile
v1.03 (June 29, 2016)
See what files are opened remotely.
PsGetSid
v1.45 (June 29, 2016)
Displays the SID of a computer or a user.
PsInfo
v1.78 (June 29, 2016)
Obtain information about a system.
PsKill
v1.16 (June 29, 2016)
Terminate local or remote processes.
PsPing
v2.01 (January 29, 2014)
Measure network performance.
PsList
v1.4 (June 29, 2016)
Show information about processes and threads.
PsLoggedOn
v1.35 (June 29, 2016)
Show users logged on to a system.
PsLogList
v2.8 (June 29, 2016)
Dump event log records.
PsPasswd
v1.24 (June 29, 2016)
Changes account passwords.
PsService
v2.25 (June 29, 2016)
View and control services.
PsShutdown
v2.52 (December 4, 2006)
Shuts down and optionally reboots a computer.
PsSuspend
v1.07 (June 29, 2016)
Suspend and resume processes.
PsTools
v2.45 (July 4, 2016)
The PsTools suite includes command-line utilities for listing the processes running on local or remote computers, running processes remotely, rebooting computers, dumping event logs, and more.
RAMMap
v1.51 (May 31, 2018)
An advanced physical memory usage analysis utility that presents usage information in different ways on its several different tabs.
RegDelNull
v1.11 (July 4, 2016)
Scan for and delete Registry keys that contain embedded null-characters that are otherwise undeleteable by standard Registry-editing tools.
Registry Usage (RU.md)
v1.2 (July 4, 2016)
View the registry space usage for the specified registry key.
RegJump
v1.1 (April 20, 2015)
Jump to the registry path you specify in Regedit.
SDelete
v2.01 (February 13, 2018)
Securely overwrite your sensitive files and cleanse your free space of previously deleted files using this DoD-compliant secure delete program.
ShareEnum
v1.6 (November 1, 2006)
Scan file shares on your network and view their security settings to close security holes.
ShellRunas
v1.01 (February 28, 2008)
Launch programs as a different user via a convenient shell context-menu entry.
Sigcheck
v2.80 (June 24, 2020)
Dump file version information and verify that images on your system are digitally signed.
Streams
v1.6 (July 4, 2016)
Reveal NTFS alternate streams.
Strings
v2.53 (July 4, 2016)
Search for ANSI and UNICODE strings in binary images.
Sync
v2.2 (July 4, 2016)
Flush cached data to disk.
Sysmon
v12.0 (September 17, 2020)
Monitors and reports key system activity via the Windows event log.
TCPView
v3.05 (July 25, 2011)
Active socket command-line viewer.
VMMap
v3.26 (June 11, 2019)
VMMap is a process virtual and physical memory analysis utility.
VolumeId
v2.1 (July 4, 2016)
Set Volume ID of FAT or NTFS drives.
Whois
v1.20 (December 11, 2019)
See who owns an Internet address.
WinObj
v2.22 (February 14, 2011)
The ultimate Object Manager namespace viewer is here.
ZoomIt
v4.52 (December 11, 2019)
Presentation utility for zooming and drawing on the screen.
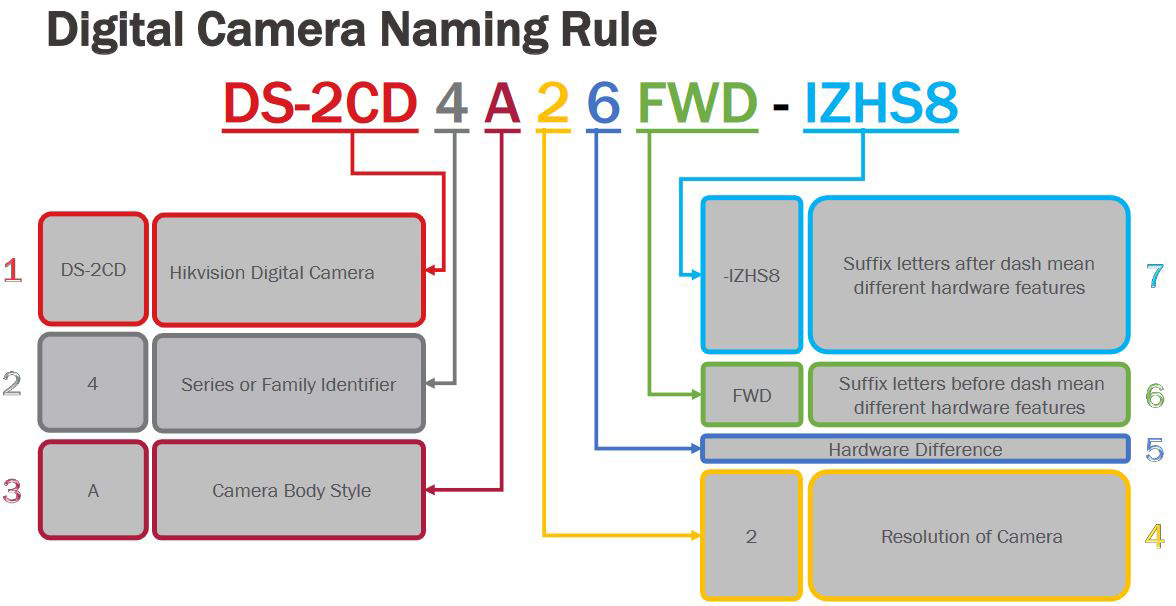
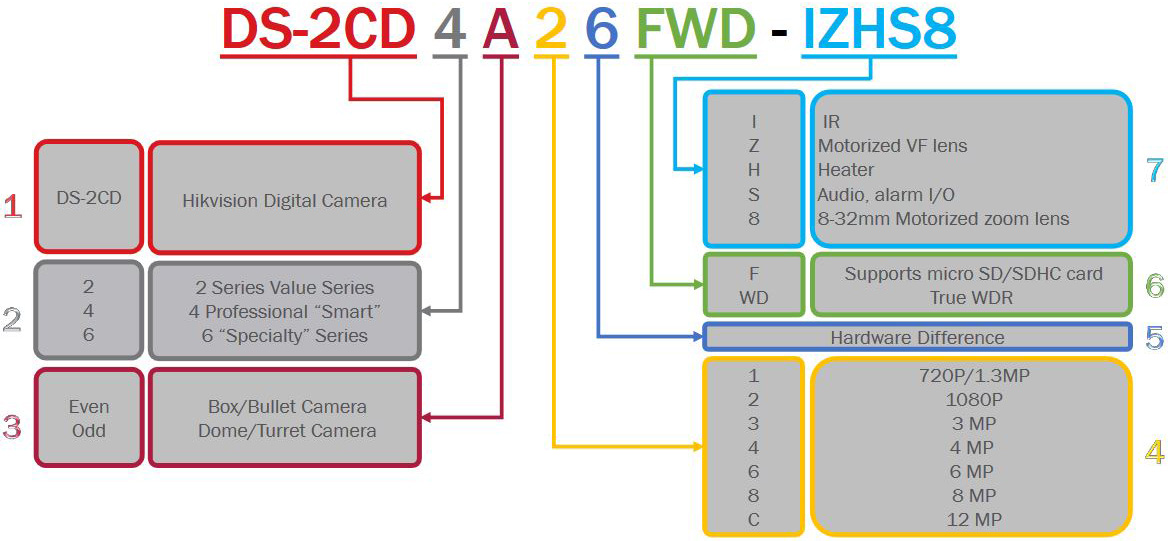
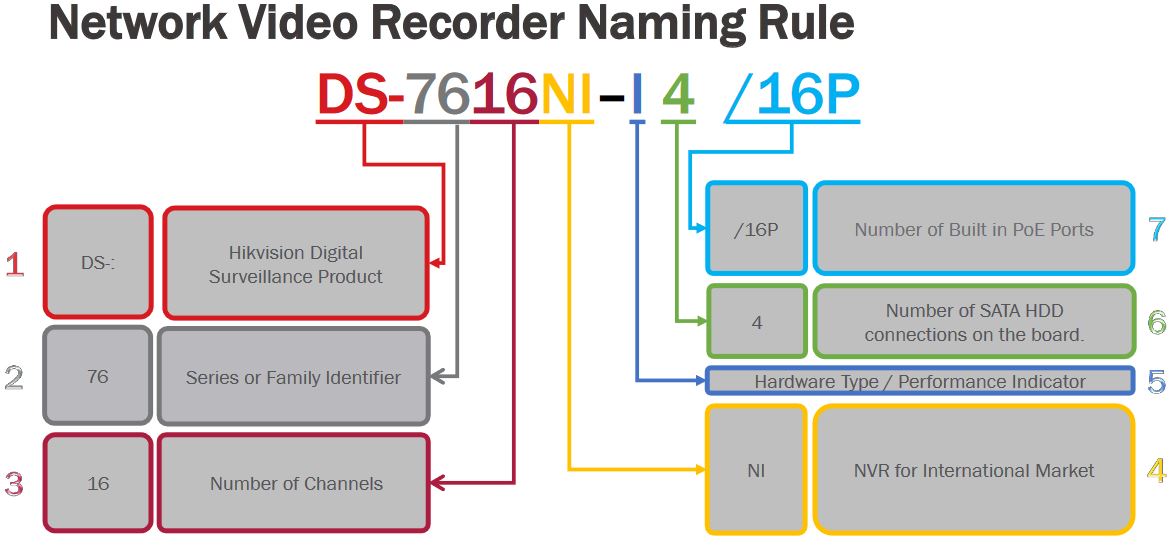
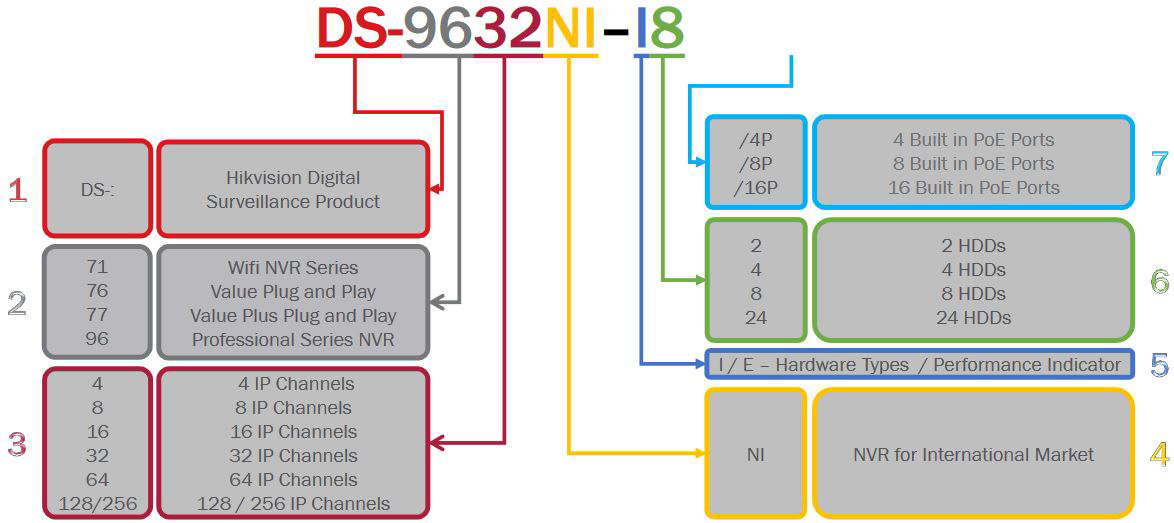
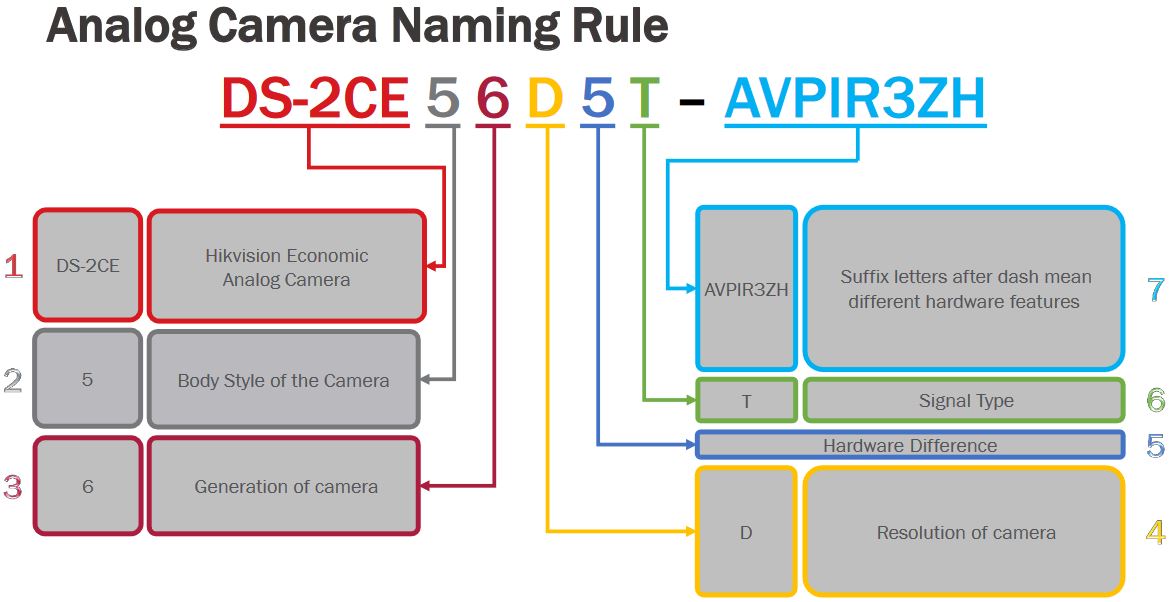
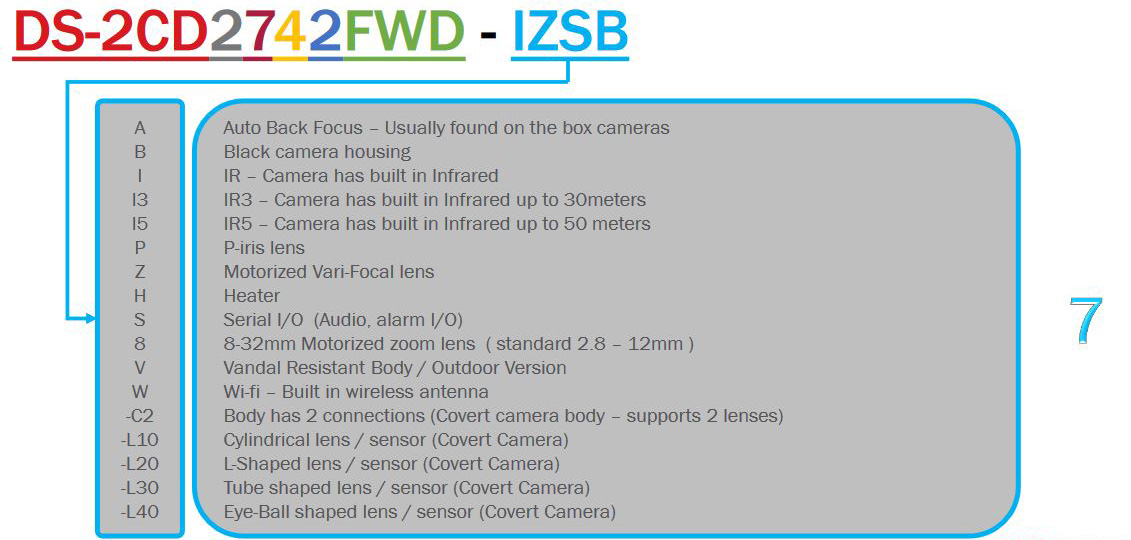 To put this into practice, DS-2CD2123G0-I is an 2MP entry level outdoor dome camera with IR. While DS-2CD2635FWD-IZS is a 3MP bullet camera with IR, motorized varifocal lens and I/O port.
To put this into practice, DS-2CD2123G0-I is an 2MP entry level outdoor dome camera with IR. While DS-2CD2635FWD-IZS is a 3MP bullet camera with IR, motorized varifocal lens and I/O port.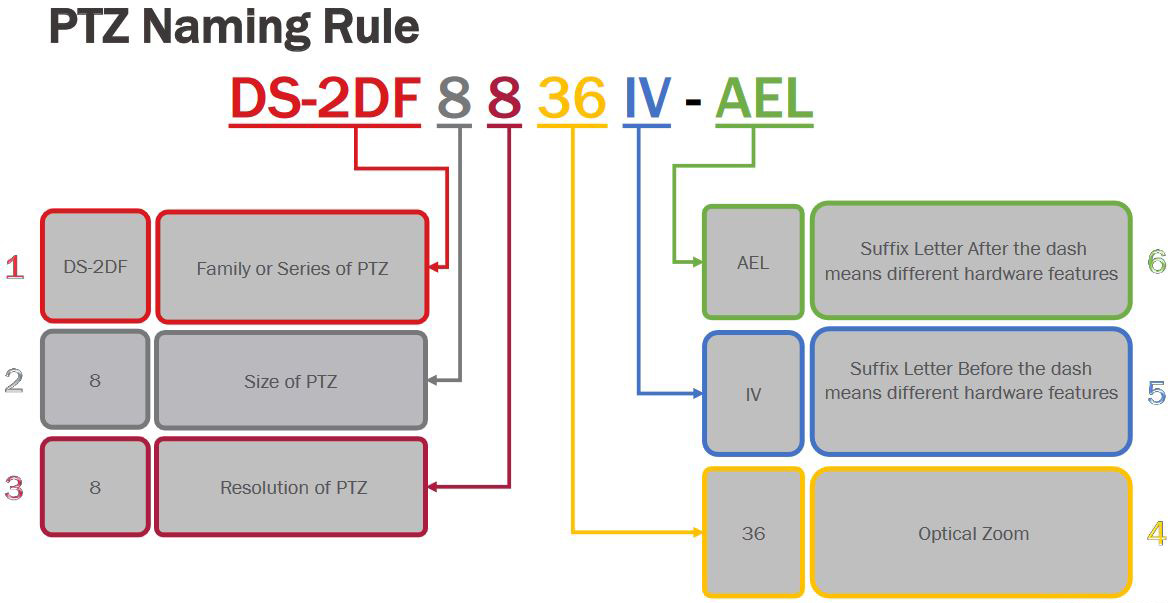
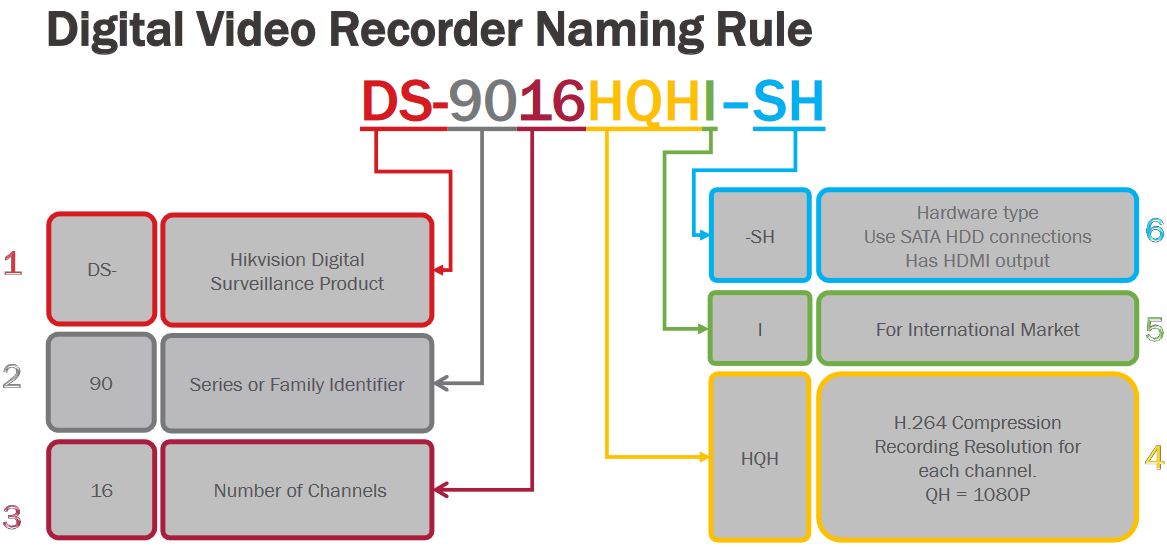
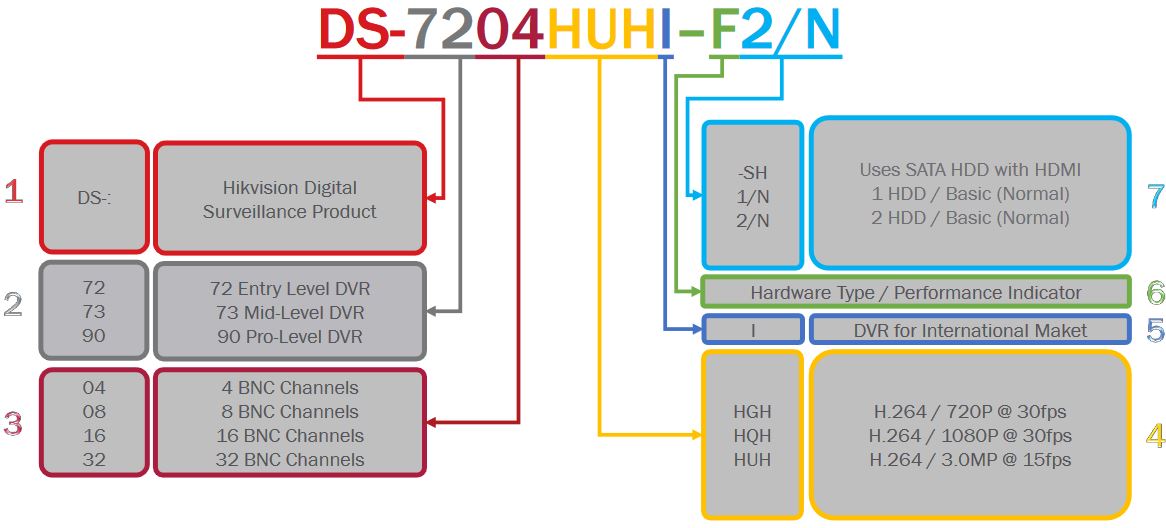
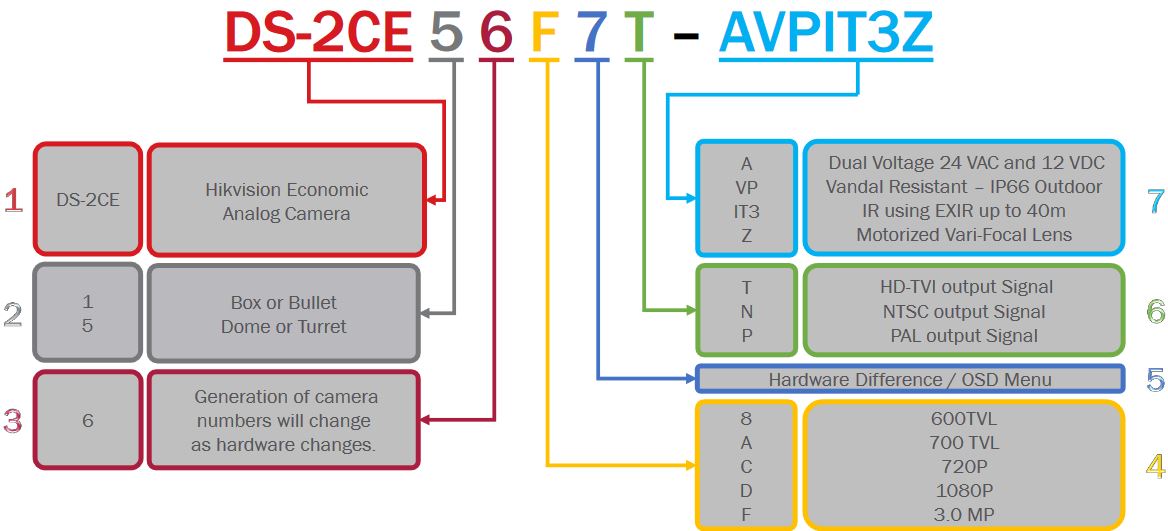
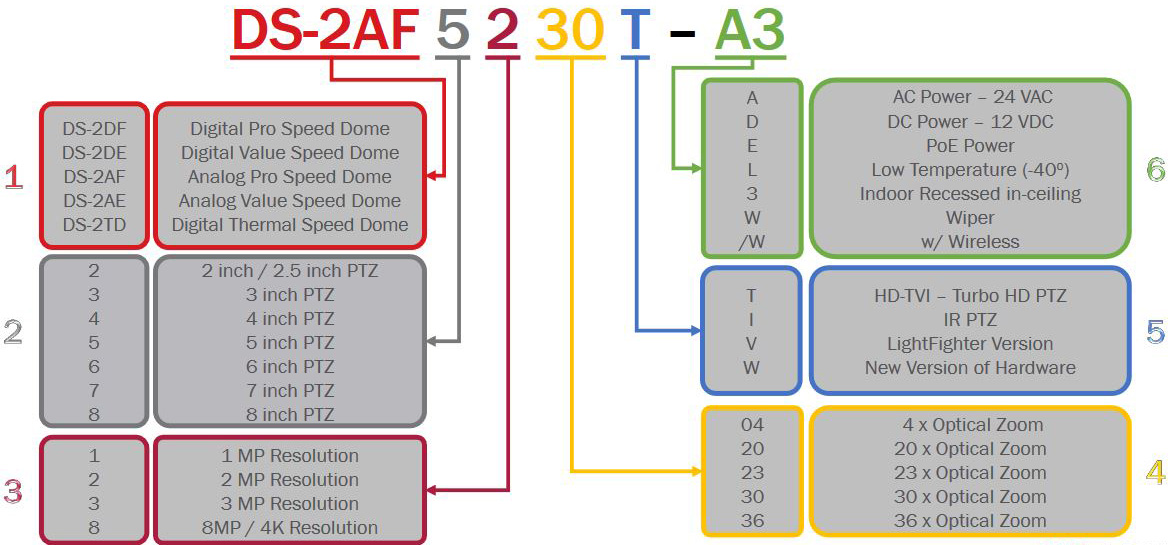 For example the DS-2DF8225IX-AELW camera is a 8” 2MP advanced PTZ camera with 25x optical zoom and IR, which can operate in low temperatures. While the DS-2DE4225IW-DE is a 4″ 2MP PTZ with 25x optical zoom.
For example the DS-2DF8225IX-AELW camera is a 8” 2MP advanced PTZ camera with 25x optical zoom and IR, which can operate in low temperatures. While the DS-2DE4225IW-DE is a 4″ 2MP PTZ with 25x optical zoom.